Induction of interferon-λ contributes to Toll-like receptor-3-activated hepatic stellate cell-mediated hepatitis C virus inhibition in hepatocytes
- PMID: 23647955
- PMCID: PMC3648885
- DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12040
Induction of interferon-λ contributes to Toll-like receptor-3-activated hepatic stellate cell-mediated hepatitis C virus inhibition in hepatocytes
Abstract
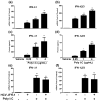
There is limited information about the role of hepatic stellate cells (HSC) in liver innate immunity against hepatitis C virus (HCV). We thus examined whether HSC can produce antiviral factors that inhibit HCV replication in human hepatocytes. HSC expressed functional Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR-3), which could be activated by its ligand, polyinosine-polycytidylic acid (poly I:C), leading to the induction of interferon-λ (IFN-λ) at both mRNA and protein levels. TLR-3 signalling of HSC also induced the expression of IFN regulatory factor 7 (IRF-7), a key regulator of IFN signalling pathway. When HCV JFH-1-infected Huh7 cells were co-cultured with HSC activated with poly I:C or incubated in media conditioned with supernatant (SN) from poly I:C-activated HSC, HCV replication was significantly suppressed. This HSC SN action on HCV inhibition was mediated through IFN-λ, which was evidenced by the observation that antibody to IFN-λ receptors could neutralize the HSC-mediated anti-HCV effect. The role of IFN-λ in HSC-mediated anti-HCV activity is further supported by the observation that HSC SN treatment induced the expression of IRF-7 and IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs), OAS-1 and MxA in HCV-infected Huh7 cells. These observations indicate that HSC may be a key regulatory bystander, participating in liver innate immunity against HCV infection using an IFN-λ-dependent mechanism.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFILCT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

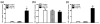
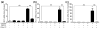

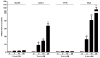

Similar articles
-
Retinoic acid inducible gene-I (RIG-I) signaling of hepatic stellate cells inhibits hepatitis C virus replication in hepatocytes.Innate Immun. 2013;19(2):193-202. doi: 10.1177/1753425912460414. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Innate Immun. 2013. PMID: 23060457 Free PMC article.
-
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate enhances poly I:C-induced interferon-λ1 production and inhibits hepatitis C virus replication in hepatocytes.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug 28;23(32):5895-5903. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5895. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28932081 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus impairs TLR3 signaling and inhibits IFN-λ 1 expression in human hepatoma cell line.Innate Immun. 2014 Jan;20(1):3-11. doi: 10.1177/1753425913478991. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Innate Immun. 2014. PMID: 23529855 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic stellate cells, liver innate immunity, and hepatitis C virus.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Aug;28 Suppl 1(0 1):112-5. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12023. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23855305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-step regulation of interferon induction by hepatitis C virus.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2013 Apr;61(2):127-38. doi: 10.1007/s00005-012-0214-x. Epub 2013 Jan 5. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2013. PMID: 23292079 Review.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps promote MASH fibrosis by metabolic reprogramming of HSC.Hepatology. 2025 Mar 1;81(3):947-961. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000762. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Hepatology. 2025. PMID: 38266270 Free PMC article.
-
Immunopathogenesis of Hepatitis C Virus Infection.Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2015 Dec;44(4):735-60. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2015.07.004. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2015. PMID: 26600217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like receptor 3-activated macrophages confer anti-HCV activity to hepatocytes through exosomes.FASEB J. 2016 Dec;30(12):4132-4140. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600696R. Epub 2016 Sep 7. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 27605546 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of interferon signaling and HCV‑RNA replication by extracellular matrix.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Aug;42(2):957-965. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3693. Epub 2018 May 18. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29786754 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Host⁻Virus Interaction and Mechanisms of Viral Persistence.Cells. 2019 Apr 25;8(4):376. doi: 10.3390/cells8040376. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31027278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Geerts A. History, heterogeneity, developmental biology, and functions of quiescent hepatic stellate cells. Semin Liver Dis. 2001;21(3):311–35. - PubMed
-
- Senoo H. Structure and function of hepatic stellate cells. Med Electron Microsc. 2004;37(1):3–15. - PubMed
-
- Winau F, Hegasy G, Weiskirchen R, et al. Ito cells are liver-resident antigen-presenting cells for activating T cell responses. Immunity. 2007;26(1):117–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

