Actuators based on liquid crystalline elastomer materials
- PMID: 23648966
- PMCID: PMC3697106
- DOI: 10.1039/c3nr00037k
Actuators based on liquid crystalline elastomer materials
Abstract
Liquid crystalline elastomers (LCEs) exhibit a number of remarkable physical effects, including the unique, high-stroke reversible mechanical actuation when triggered by external stimuli. This article reviews some recent exciting developments in the field of LCE materials with an emphasis on their utilization in actuator applications. Such applications include artificial muscles, industrial manufacturing, health and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). With suitable synthetic and preparation pathways and well-controlled actuation stimuli, such as heat, light, electric and magnetic fields, excellent physical properties of LCE materials can be realized. By comparing the actuating properties of different systems, general relationships between the structure and the properties of LCEs are discussed. How these materials can be turned into usable devices using interdisciplinary techniques is also described.
Figures










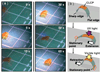
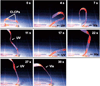
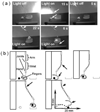

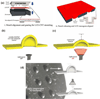



References
-
- Ionov L. J. Mater. Chem. 2010;20:3382.
-
- Lendlein A. J. Mater. Chem. 2010;20:3332.
-
- Yu Y, Ikeda T. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2006;45:5416. - PubMed
-
- Cheng F, Zhang Y, Yin R, Yu Y. J. Mater. Chem. 2010;20:4888.
-
- Warner M, Terentjev EM. Liquid Crystal Elastomers. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

