Characteristics and outcomes of patients with vasoplegic versus tissue dysoxic septic shock
- PMID: 23649098
- PMCID: PMC3982587
- DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318298836d
Characteristics and outcomes of patients with vasoplegic versus tissue dysoxic septic shock
Abstract
Background: The current consensus definition of septic shock requires hypotension after adequate fluid challenge or vasopressor requirement. Some patients with septic shock present with hypotension and hyperlactatemia greater than 2 mmol/L (tissue dysoxic shock), whereas others have hypotension alone with normal lactate (vasoplegic shock).
Objective: The objective of this study was to determine differences in outcomes of patients with tissue dysoxic versus vasoplegic septic shock.
Methods: This was a secondary analysis of a large, multicenter randomized controlled trial. Inclusion criteria were suspected infection, two or more systemic inflammatory response criteria, and systolic blood pressure less than 90 mmHg after a fluid bolus. Patients were categorized by presence of vasoplegic or tissue dysoxic shock. Demographics and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment scores were evaluated between the groups. The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality.
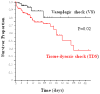
Results: A total of 247 patients were included, 90 patients with vasoplegic shock and 157 with tissue dysoxic shock. There were no significant differences in age, race, or sex between the vasoplegic and tissue dysoxic shock groups. The group with vasoplegic shock had a lower initial Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score than did the group with tissue dysoxic shock (5.5 vs. 7.0 points; P = 0.0002). The primary outcome of in-hospital mortality occurred in 8 (9%) of 90 patients with vasoplegic shock compared with 41 (26%) of 157 in the group with tissue dysoxic shock (proportion difference, 17%; 95% confidence interval, 7%-26%; P < 0.0001; log-rank test P = 0.02). After adjusting for confounders, tissue dysoxic shock remained an independent predictor of in-hospital mortality.
Conclusions: In this analysis of patients with septic shock, we found a significant difference in in-hospital mortality between patients with vasoplegic versus tissue dysoxic septic shock. These findings suggest a need to consider these differences when designing future studies of septic shock therapies.
References
-
- Angus D, Linde-Zwirble W, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky M. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Wang HE, Shapiro NI, Angus DC, Yealy DM. National estimates of severe sepsis in United States emergency departments. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:1928–1936. - PubMed
-
- Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:1250–1256. - PubMed
-
- Mikkelsen M, Miltiades A, Gaieski D, et al. Serum Lactate is Associated with Mortality in Severe Sepsis Independent of Organ Failure and Shock. Crit Care Med. 2009;37:1670–1677. - PubMed
-
- Song YH, Shin TG, Kang MJ, et al. Predicting factors associated with clinical deterioration in sepsis patients with intermediate levels of serum lactate. Shock. 2012;38:249–255. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical