ATF4 promotes bone angiogenesis by increasing VEGF expression and release in the bone environment
- PMID: 23649506
- PMCID: PMC4394202
- DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.1958
ATF4 promotes bone angiogenesis by increasing VEGF expression and release in the bone environment
Abstract
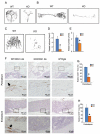
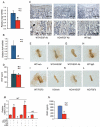
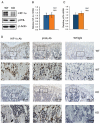
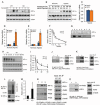
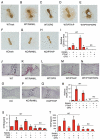
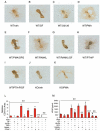
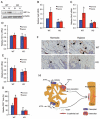
Activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) is a critical transcription factor for bone remodeling; however, its role in bone angiogenesis has not been established. Here we show that ablation of the Atf4 gene expression in mice severely impaired skeletal vasculature and reduced microvascular density of the bone associated with dramatically decreased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in osteoblasts located on bone surfaces. Results from in vivo studies revealed that hypoxia/reoxygenation induction of HIF-1α and VEGF expression leading to bone angiogenesis, a key adaptive response to hypoxic conditions, was severely compromised in mice lacking the Atf4 gene. Loss of ATF4 completely prevented endothelial sprouting from embryonic metatarsals, which was restored by addition of recombinant human VEGF protein. In vitro studies revealed that ATF4 promotion of HIF-1α and VEGF expression in osteoblasts was highly dependent upon the presence of hypoxia. ATF4 interacted with HIF-1α in hypoxic osteoblasts, and loss of ATF4 increased HIF-1α ubiquitination and reduced its protein stability without affecting HIF-1α mRNA stability and protein translation. Loss of ATF4 increased the binding of HIF-1α to prolyl hydroxylases, the enzymes that hydroxylate HIF-1a protein and promote its proteasomal degradation via the pVHL pathway. Furthermore, parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) and receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL), both well-known activators of osteoclasts, increased release of VEGF from the bone matrix and promoted angiogenesis through the protein kinase C- and ATF4-dependent activation of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. Thus, ATF4 is a new key regulator of the HIF/VEGF axis in osteoblasts in response to hypoxia and of VEGF release from bone matrix, two critical steps for bone angiogenesis.
Keywords: ANGIOGENESIS; ATF4; BONE; OSTEOBLASTS; OSTEOCLASTS; VEGF.
© 2013 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Figures
Comment in
-
ATF4 and HIF-1α in bone: an intriguing relationship.J Bone Miner Res. 2013 Sep;28(9):1866-9. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2045. J Bone Miner Res. 2013. PMID: 23873659 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Salidroside improves angiogenesis-osteogenesis coupling by regulating the HIF-1α/VEGF signalling pathway in the bone environment.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Oct 5;884:173394. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173394. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32730833
-
Prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors protect from the bone loss in ovariectomy rats by increasing bone vascularity.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 May;69(1):141-9. doi: 10.1007/s12013-013-9780-8. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014. PMID: 24242187
-
Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha pathway accelerates bone regeneration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jan 15;105(2):686-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708474105. Epub 2008 Jan 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18184809 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of hypoxia sensor--HIF-1α in VEGF gene activation. Implications for angiogenesis and tissue injury healing.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(1):90-7. doi: 10.2174/092986712803413944. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22300081 Review.
-
Role of HIF-1alpha in skeletal development.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Mar;1192:322-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05238.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20392254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wnt3a involved in the mechanical loading on improvement of bone remodeling and angiogenesis in a postmenopausal osteoporosis mouse model.FASEB J. 2019 Aug;33(8):8913-8924. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802711R. Epub 2019 Apr 24. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31017804 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: a novel targeted approach to repair bone defects by regulating osteogenesis and angiogenesis.J Transl Med. 2023 Jul 18;21(1):480. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04328-8. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37464413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SMAD-specific E3 ubiquitin ligase 2 promotes angiogenesis by facilitating PTX3 degradation in MSCs from patients with ankylosing spondylitis.Stem Cells. 2021 May;39(5):581-599. doi: 10.1002/stem.3332. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 33547700 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological mechanism of acute bone loss after fracture.J Adv Res. 2023 Jul;49:63-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.08.019. Epub 2022 Sep 15. J Adv Res. 2023. PMID: 36115662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the ER-Induced UPR Pathway and the Efficacy of Its Inhibitors and Inducers in the Inhibition of Tumor Progression.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Feb 3;2019:5729710. doi: 10.1155/2019/5729710. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 30863482 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maes C, Carmeliet P, Moermans K, Stockmans I, Smets N, Collen D, Bouillon R, Carmeliet G. Impaired angiogenesis and endochondral bone formation in mice lacking the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms VEGF164 and VEGF188. Mech Dev. 2002;111:61–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

