Identification of a secondary promoter within the human B cell receptor component gene hCD79b
- PMID: 23649625
- PMCID: PMC3689977
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.461988
Identification of a secondary promoter within the human B cell receptor component gene hCD79b
Abstract
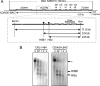
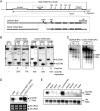
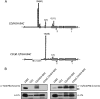
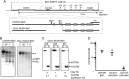
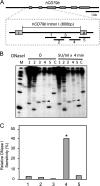
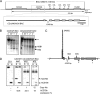
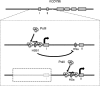
The human B cell-specific protein, CD79b (also known as Igβ and B29) constitutes an essential signal transduction component of the B cell receptor. Although its function is central to the triggering of B cell terminal differentiation in response to antigen stimulation, the transcriptional determinants that control CD79b gene expression remain poorly defined. In the present study, we explored these determinants using a series of hCD79b transgenic mouse models. Remarkably, we observed that the previously described hCD79b promoter along with its associated enhancer elements and first exon could be deleted without appreciable loss of hCD79b transcriptional activity or tissue specificity. In this deletion setting, a secondary promoter located within exon 2 maintained full levels and specificity of hCD79b transcription. Of note, this secondary promoter was also active, albeit at lower levels, in the wild-type hCD79b locus. The activity of the secondary promoter was dependent on the action(s) of a conserved sequence element mapping to a chromatin DNase I hypersensitive site located within intron 1. mRNA generated from this secondary promoter is predicted to encode an Igβ protein lacking a signal sequence and thus unable to serve normal B cell receptor function. Although the physiologic role of the hCD79b secondary promoter and its encoded protein remain unclear, the current data suggest that it has the capacity to play a role in normal as well as pathologic states in B cell proliferation and function.
Keywords: B Cell; DNase I Hypersensitive Site; Gene Expression; Immunology; Secondary Promoter; Transcription Enhancers; Transcription Promoter; Transgenic Mice; hCD79b.
Figures


References
-
- Benschop R. J., Cambier J. C. (1999) B cell development. Signal transduction by antigen receptors and their surrogates. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 11, 143–151 - PubMed
-
- Calame K. L., Lin K. I., Tunyaplin C. (2003) Regulatory mechanisms that determine the development and function of plasma cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21, 205–230 - PubMed
-
- Huang X., Takata K., Sato Y., Tanaka T., Ichimura K., Tamura M., Oka T., Yoshino T. (2011) Downregulation of the B-cell receptor signaling component CD79b in plasma cell myeloma. A possible post-transcriptional regulation. Pathol. Int. 61, 122–129 - PubMed
-
- Dobbs A. K., Yang T., Farmer D., Kager L., Parolini O., Conley M. E. (2007) Cutting edge. A hypomorphic mutation in Igβ. J. Immunol. 179, 2055–2059 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

