Coping with violence: a comprehensive framework and implications for understanding resilience
- PMID: 23649832
- PMCID: PMC7238431
- DOI: 10.1177/1524838013487806
Coping with violence: a comprehensive framework and implications for understanding resilience
Abstract
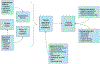
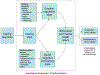
Interpersonal violence is present at all levels of influence in the social ecology and can have comprehensive and devastating effects on child and adolescent development through multiple simultaneous channels of exposure. Children's experiences with violence have been linked with a range of behavioral and mental health difficulties including posttraumatic stress disorder and aggressive behavior. In this article, we offer a conceptual framework delineating the ways in which children and adolescents might encounter violence, and a theoretical integration describing how violence might impact mental and behavioral health outcomes through short- and long-term processes. We propose that coping reactions are fundamental to the enduring effects of violence exposure on their psychosocial development and functioning. Finally, we discuss the manner in which coping efforts can support resilience among children exposed to violence and suggest new directions for research and preventive intervention aimed at optimizing outcomes for children at risk of exposure.
Keywords: community violence; domestic violence; violence exposure.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contextualizing community violence and its effects: an ecological model of parent-child interdependent coping.J Interpers Violence. 2005 Jul;20(7):855-71. doi: 10.1177/0886260505276833. J Interpers Violence. 2005. PMID: 15914706 Review.
-
The impact of exposure to domestic violence on children and young people: a review of the literature.Child Abuse Negl. 2008 Aug;32(8):797-810. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2008.02.004. Epub 2008 Aug 26. Child Abuse Negl. 2008. PMID: 18752848
-
Applying risk and resilience models to predicting the effects of media violence on development.Adv Child Dev Behav. 2014;46:215-44. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-800285-8.00008-x. Adv Child Dev Behav. 2014. PMID: 24851351 Review.
-
Exposure to conflict and violence across contexts: relations to adjustment among Palestinian children.J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2010;39(1):103-16. doi: 10.1080/15374410903401153. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2010. PMID: 20390802 Free PMC article.
-
Violence exposure and psychopathology in urban youth: the mediating role of posttraumatic stress.J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2007 Aug;35(4):578-93. doi: 10.1007/s10802-007-9114-7. Epub 2007 Feb 27. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2007. PMID: 17333360
Cited by
-
Predictive accuracy of the Violence Risk Assessment Checklist for Youth in acute institutions: A prospective naturalistic multicenter study.Eur Psychiatry. 2025 Jan 13;68(1):e19. doi: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2025.3. Eur Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39801327 Free PMC article.
-
Growing Up Amid Ethno-Political Conflict: Aggression and Emotional Desensitization Promote Hostility to Ethnic Outgroups.Child Dev. 2016 Sep;87(5):1479-92. doi: 10.1111/cdev.12599. Child Dev. 2016. PMID: 27684400 Free PMC article.
-
A review of developmental research on resilience in maltreated children.Trauma Violence Abuse. 2013 Jul;14(3):222-34. doi: 10.1177/1524838013487808. Epub 2013 May 10. Trauma Violence Abuse. 2013. PMID: 23666947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exposure to violence predicts callous-unemotional traits and aggression in adolescence in the context of persistent ethnic-political conflict and violence.Aggress Behav. 2023 Nov;49(6):655-668. doi: 10.1002/ab.22103. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Aggress Behav. 2023. PMID: 37539489 Free PMC article.
-
Future Directions in Research and Intervention with Youths in Poverty.J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2018 Nov-Dec;47(6):1023-1038. doi: 10.1080/15374416.2018.1485108. Epub 2018 Jul 27. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2018. PMID: 30052089 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson CA, Berkowitz L, Donnerstein E, Huesmann LR, Johnson JD, Linz D, Malamuth N, & Wartella E (2003). The influence of media violence on youth. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 4, 81–110. - PubMed
-
- Bandura A (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social-cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
-
- Bandura A (1999). Moral disengagement in the perpetration of inhumanities. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 3, 193–209. - PubMed
-
- Bjorck JP, & Cohen LH (1993). Coping with threats, losses, and challenge. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 12, 36–72.
-
- Boxer P, Edwards-Leeper L, Goldstein SE, Musher-Eizenman D, & Dubow EF (2003). Exposure to “low-level” aggression in school: Associations with aggressive behavior, future expectations, and perceived safety. Violence and Victims, 18, 691–705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical