Identification of the nature of reading frame transitions observed in prokaryotic genomes
- PMID: 23649834
- PMCID: PMC3711429
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt274
Identification of the nature of reading frame transitions observed in prokaryotic genomes
Abstract
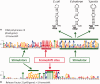
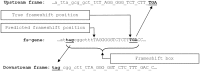
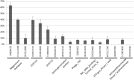
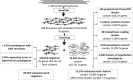
Our goal was to identify evolutionary conserved frame transitions in protein coding regions and to uncover an underlying functional role of these structural aberrations. We used the ab initio frameshift prediction program, GeneTack, to detect reading frame transitions in 206 991 genes (fs-genes) from 1106 complete prokaryotic genomes. We grouped 102 731 fs-genes into 19 430 clusters based on sequence similarity between protein products (fs-proteins) as well as conservation of predicted position of the frameshift and its direction. We identified 4010 pseudogene clusters and 146 clusters of fs-genes apparently using recoding (local deviation from using standard genetic code) due to possessing specific sequence motifs near frameshift positions. Particularly interesting was finding of a novel type of organization of the dnaX gene, where recoding is required for synthesis of the longer subunit, τ. We selected 20 clusters of predicted recoding candidates and designed a series of genetic constructs with a reporter gene or affinity tag whose expression would require a frameshift event. Expression of the constructs in Escherichia coli demonstrated enrichment of the set of candidates with sequences that trigger genuine programmed ribosomal frameshifting; we have experimentally confirmed four new families of programmed frameshifts.
Figures
References
-
- Antonov I, Borodovsky M. GeneTack: frameshift identification in protein-coding sequences by the Viterbi algorithm. J. Bioinform. Comput. Biol. 2010;8:535–551. - PubMed
-
- Sharma V, Firth AE, Antonov I, Fayet O, Atkins JF, Borodovsky M, Baranov PV. A pilot study of bacterial genes with disrupted ORFs reveals a surprising profusion of protein sequence recoding mediated by ribosomal frameshifting and transcriptional realignment. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011;28:3195–3211. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atkins JF, Gesteland RF. Recoding: Expansion of Decoding Rules Enriches Gene Expression. 1st edn. Springer; 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

