Compliance with pharmacotherapy and direct healthcare costs in patients with Parkinson's disease: a retrospective claims database analysis
- PMID: 23649891
- PMCID: PMC3717155
- DOI: 10.1007/s40258-013-0033-1
Compliance with pharmacotherapy and direct healthcare costs in patients with Parkinson's disease: a retrospective claims database analysis
Abstract
Background: Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurological disorder for which, at present, there is no cure. Current therapy is largely based on the use of dopamine agonists and dopamine replacement therapy, designed to control the signs and symptoms of the disease. The majority of current treatments are administered in tablet form and can involve multiple daily doses, which may contribute to sub-optimal compliance. Previous studies with small groups of patients suggest that non-compliance with treatment can result in poor response to therapy and may ultimately increase direct and indirect healthcare costs.
Objective: To determine the extent of non-compliance within the general PD population in the USA as well as the patient characteristics and healthcare costs associated with compliance and non-compliance.
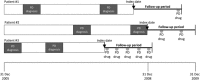
Methods: A retrospective analysis from a managed care perspective was conducted using data from the USA PharMetrics patient-centric claims database. PharMetrics claims data were complete from 31 December 2005 to 31 December 2009. Patients were included if they had at least two diagnoses for PD between 31 December 2005 and 31 December 2008, were older than 18 years of age, were continuously enrolled for at least 12 months after the date of the most recent PD diagnosis, and had no missing or invalid data. The follow-up period was the most recent 12-month block of continuous enrollment that occurred between 2006 and 2009. Patients were required to have at least one PD-related prescription within the follow-up period. The medication possession ratio (MPR) was used to categorise patients as compliant or non-compliant. Direct all-cause annual healthcare costs for patients with PD were estimated for each patient, and regression analyses were conducted to determine predictors for non-compliance.
Results: A total of 15,846 patients were included, of whom 46 % were considered to be non-compliant with their prescribed medication (MPR <0.8). Predictors of non-compliance included prescription of a medication administered in multiple daily doses (p < 0.0001), a period of <2 years since the initial PD diagnosis (p = 0.0002), a diagnosis of gastrointestinal disorder (p < 0.0001), and a diagnosis of depression (p < 0.0001). Non-compliance was also found to be related to age, with a lower odds of non-compliance in patients aged 41-80 years than in patients aged ≥81 years (p < 0.05). Although total drug mean costs were higher for compliant patients than non-compliant patients (driven mainly by the cost of PD-related medications), the mean costs associated with emergency room and inpatient visits were higher for patients non-compliant with their prescribed medication. Overall, the total all-cause annual healthcare mean cost was lower for compliant ($77,499) than for non-compliant patients ($84,949; p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Non-compliance is prevalent within the general USA PD population and is associated with a recent PD diagnosis, certain comorbidities, and multiple daily treatment dosing. Non-compliance may increase the burden on the healthcare system because of greater resource usage compared with the compliant population. Treatments that require fewer daily doses may have the potential to improve compliance, which in turn could reduce the economic burden associated with PD.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prevalence and cost of medication nonadherence in Parkinson's disease: evidence from administrative claims data.Mov Disord. 2010 Mar 15;25(4):474-80. doi: 10.1002/mds.22999. Mov Disord. 2010. PMID: 20131374
-
Duloxetine compliance and its association with healthcare costs among patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain.J Med Econ. 2009 Sep;12(3):192-202. doi: 10.3111/13696990903240559. J Med Econ. 2009. PMID: 19705975
-
Cost and consequences of noncompliance with osteoporosis treatment among women initiating therapy.Curr Med Res Opin. 2015 Apr;31(4):757-65. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2015.1016605. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Curr Med Res Opin. 2015. PMID: 25661017
-
Medication adherence in patients with Parkinson's disease.CNS Drugs. 2015 Jan;29(1):47-53. doi: 10.1007/s40263-014-0220-0. CNS Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25503824 Review.
-
[Cost-effectiveness analysis of schizophrenic patient care settings: impact of an atypical antipsychotic under long-acting injection formulation].Encephale. 2005 Mar-Apr;31(2):235-46. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(05)82390-5. Encephale. 2005. PMID: 15959450 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Effect of Pillbox Organizers with Alarms on Adherence to Pharmacotherapy in Parkinson Disease Patients Taking Three and More Daily Doses of Dopaminergic Medications.J Pers Med. 2022 Jan 28;12(2):179. doi: 10.3390/jpm12020179. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35207667 Free PMC article.
-
Persistence and adherence to levodopa adjunct medications in elderly patients with Parkinson's disease: a retrospective cohort study using a Japanese claims database.Front Neurol. 2025 Apr 10;16:1560431. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1560431. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40276471 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription pattern of anti-Parkinson's disease drugs in Japan based on a nationwide medical claims database.eNeurologicalSci. 2020 Jul 16;20:100257. doi: 10.1016/j.ensci.2020.100257. eCollection 2020 Sep. eNeurologicalSci. 2020. PMID: 32775705 Free PMC article.
-
Medication adherence and costs of medical care among patients with Parkinson's disease: an observational study using electronic medical records.BMC Public Health. 2024 Apr 30;24(1):1202. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18431-y. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38689223 Free PMC article.
-
A Qualitative Study on Perspectives of Parkinson's Disease Medications: Insights from Patient Focus Groups.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2024 Sep 18;18:1919-1928. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S473991. eCollection 2024. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2024. PMID: 39310087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Rijk MC, Launer LJ, Berger K, Breteler MM, Dartigues JF, Baldereschi M, et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in Europe: a collaborative study of population-based cohorts. Neurologic Diseases in the Elderly Research Group. Neurology. 2000;54(11 Suppl 5):S21–3. - PubMed
-
- Canadian Neurological Sciences Federation. Canadian guidelines on Parkinson’s disease. Can J Neurol Sci 2012;39(Suppl 4):S1–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

