Thrombospondin-4 contributes to spinal cord injury-induced changes in nociception
- PMID: 23649982
- PMCID: PMC3762950
- DOI: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00326.x
Thrombospondin-4 contributes to spinal cord injury-induced changes in nociception
Abstract
Background: Our previous data have indicated that nerve injury-induced up-regulation of thrombospondin-4 (TSP4) proteins in dorsal spinal cord plays a causal role in neuropathic pain state development in a spinal nerve ligation model. To investigate whether TSP4 proteins also contribute to the development of centrally mediated changes in nociception after spinal cord injury (SCI), we investigated whether SCI induced TSP4 dysregulation, and if so, whether this change correlated with changes in nociception in a T9 spinal cord contusion injury model.
Methods: Behavioural sensitivity to mechanical, thermal stimuli and locomotor function recovery were tested blindly in SCI or sham rats post-injury. Intrathecal antisense or mismatch control oligodeoxynucleotides were used to treat SCI rats with nociceptive hyperreflexia, and Western blots were used to measure TSP4 protein levels in dorsal spinal cord samples.
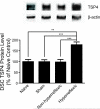
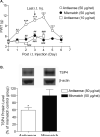
Results: SCI induced below-level hindpaw hypersensitivity to stimuli. TSP4 protein levels are up-regulated in dorsal spinal cord of SCI rats with nociceptive hyperreflexia, but not in SCI rats without nociceptive hyperreflexia. There was no significant difference in motor function recovery post-injury between SCI rats with or without nociceptive hyperreflexia. Intrathecal treatment with TSP4 antisense, but not mismatch control, oligodeoxynucleotides led to reversal of injury-induced TSP4 up-regulation and nociceptive hyperreflexia in SCI rats.
Conclusions: SCI leads to TSP4 up-regulation in lumbar spinal cord that may play a critical role in mediating centrally mediated behavioural hypersensitivity. Blocking this pathway may be helpful in management of SCI-induced changes in nociception.
© 2013 European Federation of International Association for the Study of Pain Chapters.
Figures

References
-
- Ataoglu E, Tiftik T, Kara M, Tunc H, Ersoz M, Akkus S. Effects of chronic pain on quality of life and depression in patients with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2012;51:23–26. - PubMed
-
- Baastrup C, Maersk-Moller CC, Nyengaard JR, Jensen TS, Finnerup NB. Spinal-, brainstem- and cerebrally mediated responses at- and below-level of a spinal cord contusion in rats: evaluation of pain-like behavior. Pain. 2010;151:670–679. - PubMed
-
- Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein P, Agah A, Kyriakides TR. The role of thrombospondins 1 and 2 in the regulation of cell-matrix interactions, collagen fibril formation, and the response to injury. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36:1115–1125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

