Therapeutic destruction of insulin receptor substrates for cancer treatment
- PMID: 23651636
- PMCID: PMC4391644
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3385
Therapeutic destruction of insulin receptor substrates for cancer treatment
Abstract
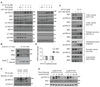
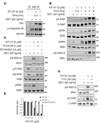
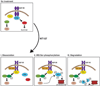
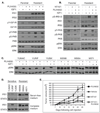
Insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 (IRS1/2) mediate mitogenic and antiapoptotic signaling from insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-IR), insulin receptor (IR), and other oncoproteins. IRS1 plays a central role in cancer cell proliferation, its expression is increased in many human malignancies, and its upregulation mediates resistance to anticancer drugs. IRS2 is associated with cancer cell motility and metastasis. Currently, there are no anticancer agents that target IRS1/2. We present new IGF-IR/IRS-targeted agents (NT compounds) that promote inhibitory Ser-phosphorylation and degradation of IRS1 and IRS2. Elimination of IRS1/2 results in long-term inhibition of IRS1/2-mediated signaling. The therapeutic significance of this inhibition in cancer cells was shown while unraveling a novel mechanism of resistance to B-RAF(V600E/K) inhibitors. We found that IRS1 is upregulated in PLX4032-resistant melanoma cells and in cell lines derived from patients whose tumors developed PLX4032 resistance. In both settings, NT compounds led to the elimination of IRS proteins and evoked cell death. Treatment with NT compounds in vivo significantly inhibited the growth of PLX4032-resistant tumors and displayed potent antitumor effects in ovarian and prostate cancers. Our findings offer preclinical proof-of-concept for IRS1/2 inhibitors as cancer therapeutics including PLX4032-resistant melanoma. By the elimination of IRS proteins, such agents should prevent acquisition of resistance to mutated-B-RAF inhibitors and possibly restore drug sensitivity in resistant tumors.
©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures



References
-
- Dalmizrak O, Wu A, Chen J, Sun H, Utama FE, Zambelli D, Tran TH, Rui H, Baserga R. Insulin receptor substrate-1 regulates the transformed phenotype of BT-20 human mammary cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2124–2130. - PubMed
-
- Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades NS, McMullan CJ, Poulaki V, Shringarpure R, Akiyama M, Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Joseph M, Libermann TA, Garcia-Echeverria C, Pearson MA, Hofmann F, Anderson KC, Kung AL. Inhibition of the insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 tyrosine kinase activity as a therapeutic strategy for multiple myeloma, other hematologic malignancies, and solid tumors. Cancer Cell. 2004;5:221–230. - PubMed
-
- Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE. Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:505–518. - PubMed
-
- Ryan PD, Goss PE. The emerging role of the insulin-like growth factor pathway as a therapeutic target in cancer. Oncologist. 2008;13:16–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

