Topical diacerein for epidermolysis bullosa: a randomized controlled pilot study
- PMID: 23651789
- PMCID: PMC3655927
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-8-69
Topical diacerein for epidermolysis bullosa: a randomized controlled pilot study
Abstract
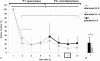
Blistering in epidermolysis bullosa simplex type Dowling-Meara (EBS-DM) is associated with an inflammatory phenotype, which can be disrupted by diacerein in vitro. In this pilot study we hypothesized, that a topical formulation of diacerein 1% reduces blistering. Five patients initially applied diacerein underneath both armpits. Then, each participant received 1% diacerein-cream for one armpit, and placebo for the other (randomized withdrawal). The number of blisters was reduced significantly (left: -78%; right: -66% of baseline) within two weeks and remained significantly below the initial level even during withdrawal in four patients. These findings point to a relevant effect of diacerein and provide important information for a confirmative study.
Figures

References
-
- Morley SM, D'Alessandro M, Sexton C, Rugg EL, Navsaria H, Shemanko CS, Huber M, Hohl D, Heagerty AI, Leigh IM, Lane EB. Generation and characterization of epidermolysis bullosa simplex cell lines: scratch assays show faster migration with disruptive keratin mutations. Br J Dermatol. 2003;149:46–58. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05493.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Verbruggen G. Chondroprotective drugs in degenerative joint diseases. Rheumatol. 2006;45:129–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

