Investigation of ginkgo biloba leave extracts as corrosion and Oil field microorganism inhibitors
- PMID: 23651921
- PMCID: PMC3661374
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-153X-7-83
Investigation of ginkgo biloba leave extracts as corrosion and Oil field microorganism inhibitors
Abstract
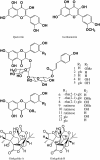
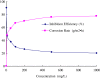
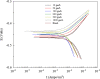
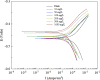
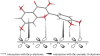
Ginkgo biloba (Ginkgoaceae), originating from China, now distributes all over the world. Wide application of Ginkgo biloba extracts is determined by the main active substances, flavonoids and terpenoids, which indicates its extracts suitable to be used as an effective corrosion inhibitor. The extracts of Ginkgo biloba leave have been investigated on the corrosion inhibition of Q235A steel with weight loss and potentiodynamic polarisation techniques. The inhibition efficiency of the extracts varies with extract concentration. The extracts inhibit corrosion mainly by adsorption mechanism. Potentiodynamic polarisation studies show that extracts are mixed type inhibitors. The antibacterial activity of the extracts against oil field microorganism (SRB, IB and TGB) was also investigated.
Figures



References
-
- Borchardt JK, Yen TF. Oil-field chemistry—enhanced recovery and production stimulation. Toronto: Ontario, Canada; 1988. pp. 608–610.
-
- Liu YR, Gao ZM, Zhang Z, Shi DF. Electrochemically aided deposition of TiO2 films on Ni-P pre-plated A3 carbon steel. Corrosion Sci Prot Technol. 2007;19:323–325.
-
- Jiang JH, Li L, Hu JX, Jiang JQ, Ma AB. New Zinc-phosphating process with RE catalyzer at low temperature for painting pretreatment of cold-rolling A3 steel sheet. Surf Technol. 2007;36(4):79–81.
-
- Sastri VS. Corrosion inhibitors principle and application. New York: John Willey & Sons; 1998. pp. 198–202.
-
- Raman A, Labine P, Quraishi MA. Reviews on corrosion inhibitor science and technology. Houstan: NACE International; 2004. 3.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

