PPARγ signaling and metabolism: the good, the bad and the future
- PMID: 23652116
- PMCID: PMC3870016
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3159
PPARγ signaling and metabolism: the good, the bad and the future
Abstract
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) are potent insulin sensitizers that act through the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) and are highly effective oral medications for type 2 diabetes. However, their unique benefits are shadowed by the risk for fluid retention, weight gain, bone loss and congestive heart failure. This raises the question as to whether it is possible to build a safer generation of PPARγ-specific drugs that evoke fewer side effects while preserving insulin-sensitizing potential. Recent studies that have supported the continuing physiologic and therapeutic relevance of the PPARγ pathway also provide opportunities to develop newer classes of molecules that reduce or eliminate adverse effects. This review highlights key advances in understanding PPARγ signaling in energy homeostasis and metabolic disease and also provides new explanations for adverse events linked to TZD-based therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
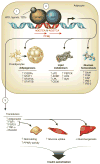
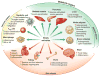
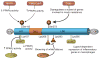
References
-
- Evans RM, Barish GD, Wang YX. PPARs and the complex journey to obesity. Nat Med. 2004;10:355–361. - PubMed
-
- Poulsen L, Siersbaek M, Mandrup S. PPARs: fatty acid sensors controlling metabolism. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012;23:631–639. - PubMed
-
- Forman BM, et al. 15-Deoxy-δ 12, 14-prostaglandin J2 is a ligand for the adipocyte determination factor PPARγ. Cell. 1995;83:803–812. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL088093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL088093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- DK090962/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL105278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK090962/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

