Design of a bioartificial pancreas
- PMID: 23652283
- PMCID: PMC3746499
- DOI: 10.1159/000345873
Design of a bioartificial pancreas
Abstract
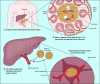
Islet transplantation has been shown to be a viable treatment option for patients afflicted with type 1 diabetes. However, the lack of availablity of human pancreases and the need to use risky immunosuppressive drugs to prevent transplant rejection remain two major obstacles to the routine use of islet transplantation in diabetic patients. Successful development of a bioartificial pancreas using the approach of microencapsulation with perm-selective coating of islets in hydrogels for graft immunoisolation holds tremendous promise for diabetic patients because it has great potential to overcome these two barriers. In this review article, we will discuss the need for a bioartificial pancreas, provide a detailed description of the microencapsulation process, and review the status of the technology in clinical development. We will also critically review the various factors that will need to be taken into consideration in order to achieve the ultimate goal of routine clinical application.
Copyright © 2013 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Bliss M. The discovery of insulin. The University of Chicago Press; 1982.
-
- Kort HD, Koning EJD, Rabelink TJ, Bruijn JA, Bajema IM. Islet transplantation in type 1 diabetes. BMJ. 2011;342:d217. - PubMed
-
- THE DIABETES CONTROL AND COMPLICATIONS TRIAL RESEARCH GROUP The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–986. - PubMed
-
- Kelly WD, Lillehei RC, Merkel FK, Idezuki Y, Goetz FC. Allotransplantation of the pancreas and duodenum along with the kidney in diabetic nephropathy. Surgery. 1967;61(6):827–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical