First-line treatment patterns and clinical outcomes in patients with HER2-positive and hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer from registHER
- PMID: 23652380
- PMCID: PMC3662840
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0414
First-line treatment patterns and clinical outcomes in patients with HER2-positive and hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer from registHER
Abstract
Background: Limited data are available describing the natural history of patients with HER2-positive and hormone receptor (HR)-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC). We examined first-line treatment patterns and clinical outcomes in patients with HER2-positive, HR-positive MBC in a real-world setting.
Methods: registHER is a prospective, observational cohort of 1,023 patients with HER2-positive MBC diagnosed within 6 months of enrollment and followed until death, disenrollment, or June 2009 (median follow-up time: 27 months). Demographics, first-line treatment patterns, and clinical outcomes were examined for 530 HER2-positive, HR-positive patients. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) times were examined. Multivariate analyses adjusted for baseline demographic and prognostic factors.
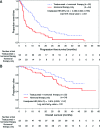
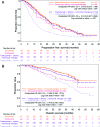
Results: HER2-positive, HR-positive patients receiving first-line trastuzumab plus hormonal therapy had significantly longer PFS times than patients who received hormonal therapy only (13.8 vs. 4.8 months; adjusted hazard ratio [HR]: 0.37, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.22-0.60); a nonsignificant reduction in OS time was observed (adjusted HR: 0.55, 95% CI: 0.27-1.14). Compared with patients who received first-line trastuzumab plus chemotherapy, patients who received first-line trastuzumab plus chemotherapy and hormonal therapy had longer median PFS times (20.4 months vs. 9.5 months; adjusted HR: 0.53, 95% CI: 0.42-0.68); a statistically significant reduction in risk of death was observed (adjusted HR: 0.50, 95% CI: 0.36-0.70). Sequential use of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy was associated with improved OS times when compared with concurrent use (adjusted PFS HR: 0.81, 95% CI: 0.54-1.21; adjusted OS HR: 0.48, 95% CI: 0.26-0.89).
Conclusions: These real-world data in patients with HER2-positive/HR-positive MBC provide evidence that, with or without chemotherapy, dual targeting of HRs and HER2 receptors is associated with significantly prolonged PFS and OS times.
Keywords: Breast cancer; HER2; Hormone receptor; Metastatic; Trastuzumab; Treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of potential conflicts of interest may be found at the end of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, et al. Human breast cancer: Correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987;235:177–182. - PubMed
-
- Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Procter M, Leyland-Jones B, et al. Trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1659–1672. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:783–792. - PubMed
-
- Brufsky A, Lembersky B, Schiffman K, et al. Hormone receptor status does not affect the clinical benefit of trastuzumab therapy for patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 2005;6:247–252. - PubMed
-
- Todorovic-Rakovic N, Neskovic-Konstantinovic Z, Nikolic-Vukosavljevic D. Cross-talk between ER and HER2 in breast carcinoma. Arch Oncol. 2006;14:146–150.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

