Can salivary phosphate levels be an early biomarker to monitor the evolvement of obesity?
- PMID: 23652556
- PMCID: PMC3896993
- DOI: 10.1159/000346793
Can salivary phosphate levels be an early biomarker to monitor the evolvement of obesity?
Abstract
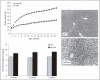
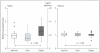
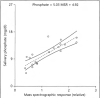
Phosphate is an essential nutrient required for important biological reactions that maintain the normal homoeostatic control of the cell. The adverse effects of phosphate metabolism in obesity have not been studied in detail, chiefly because such an association is thought to be uncommon. However, in some animal models of obesity, serum phosphate levels were noted to be higher than the nonobese controls. For example, leptin-deficient (ob/ob) mice become severely obese and have high serum phosphate levels. In this study, we analyzed the phosphate content in saliva collected from children (n = 77; 10.5 ± 1.8) to evaluate association with body mass index; there is a significant increase of salivary phosphate content in obese compared to normal-weight children (ANOVA p < 0.001). The correlation coefficient (r) between BMI and phosphate was 0.33 (p = 0.0032). Our results suggest that the human salivary phosphate level may be an early biomarker of the genesis of obesity in children. The diagnostic importance lies in the fact that the salivary phosphate level could provide a noninvasive predictive marker in the development of obesity. Further studies will be required to understand the underlying mechanism of increased salivary phosphate accumulation in obese and overweight children. Nevertheless, its occurrence without systemic changes could be of diagnostic value, particularly in monitoring evolvement of obesity.
Copyright © 2013 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The salivary levels of leptin and interleukin-6 as potential inflammatory markers in children obesity.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 3;14(1):e0210288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210288. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30605486 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated salivary C-reactive protein predicted by low cardio-respiratory fitness and being overweight in African children.Cardiovasc J Afr. 2012 Oct;23(9):501-6. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2012-058. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2012. PMID: 23108518 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of salivary secretion in normal-weight, overweight and obese children: a preliminary study: salivary composition and excessive fat tissue.Odontology. 2014 Jul;102(2):318-24. doi: 10.1007/s10266-013-0103-8. Epub 2013 Feb 10. Odontology. 2014. PMID: 23397524
-
Multihormonal control of ob gene expression and leptin secretion from cultured human visceral adipose tissue: increased responsiveness to glucocorticoids in obesity.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998 Mar;83(3):902-10. doi: 10.1210/jcem.83.3.4644. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998. PMID: 9506746 Review.
-
Clinical aspects of leptin.Vitam Horm. 1998;54:1-30. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60919-x. Vitam Horm. 1998. PMID: 9529971 Review.
Cited by
-
Salivary N1-Methyl-2-Pyridone-5-Carboxamide, a Biomarker for Uranium Uptake, in Kuwaiti Children Exhibiting Exceptional Weight Gain.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Jun 20;10:382. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00382. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31281289 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary phosphate as a biomarker for human diseases.FASEB Bioadv. 2022 Jan 3;4(2):102-108. doi: 10.1096/fba.2021-00104. eCollection 2022 Feb. FASEB Bioadv. 2022. PMID: 35141474 Free PMC article.
-
Breast Cancer and Bone Mineral Density in a U.S. Cohort of Middle-Aged Women: Associations with Phosphate Toxicity.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 21;15(20):5093. doi: 10.3390/cancers15205093. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894460 Free PMC article.
-
FGF23-induced hypophosphatemia persists in Hyp mice deficient in the WNT coreceptor Lrp6.Contrib Nephrol. 2013;180:124-37. doi: 10.1159/000346792. Epub 2013 May 3. Contrib Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23652555 Free PMC article.
-
5-Diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate (5-IP7) regulates phosphate release from acidocalcisomes and yeast vacuoles.J Biol Chem. 2018 Dec 7;293(49):19101-19112. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005884. Epub 2018 Oct 12. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30315104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haap M, Heller E, Thamer C, Tschritter O, Stefan N, Fritsche A. Association of serum phosphate levels with glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion in non-diabetic subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2006;60:734–739. - PubMed
-
- Celik N, Andiran N. The relationship between serum phosphate levels with childhood obesity and insulin resistance. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2011;24:81–83. - PubMed
-
- Tsuji K, Maeda T, Kawane T, Matsunuma A, Horiuchi N. Leptin stimulates fibroblast growth factor 23 expression in bone and suppresses renal 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 synthesis in leptin-deficient mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25:1711–1723. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

