Mass spectrometry imaging with high resolution in mass and space
- PMID: 23652571
- PMCID: PMC3656243
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-013-1097-6
Mass spectrometry imaging with high resolution in mass and space
Abstract
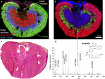
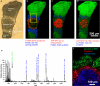
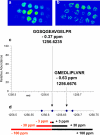
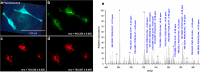
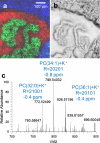
Mass spectrometry (MS) imaging links molecular information and the spatial distribution of analytes within a sample. In contrast to most histochemical techniques, mass spectrometry imaging can differentiate molecular modifications and does not require labeling of targeted compounds. We have recently introduced the first mass spectrometry imaging method that provides highly specific molecular information (high resolution and accuracy in mass) at cellular dimensions (high resolution in space). This method is based on a matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) imaging source working at atmospheric pressure which is coupled to an orbital trapping mass spectrometer. Here, we present a number of application examples and demonstrate the benefit of 'mass spectrometry imaging with high resolution in mass and space.' Phospholipids, peptides and drug compounds were imaged in a number of tissue samples at a spatial resolution of 5-10 μm. Proteins were analyzed after on-tissue tryptic digestion at 50-μm resolution. Additional applications include the analysis of single cells and of human lung carcinoma tissue as well as the first MALDI imaging measurement of tissue at 3 μm pixel size. MS image analysis for all these experiments showed excellent correlation with histological staining evaluation. The high mass resolution (R = 30,000) and mass accuracy (typically 1 ppm) proved to be essential for specific image generation and reliable identification of analytes in tissue samples. The ability to combine the required high-quality mass analysis with spatial resolution in the range of single cells is a unique feature of our method. With that, it has the potential to supplement classical histochemical protocols and to provide new insights about molecular processes on the cellular level.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

