Phase I study of pazopanib in patients with advanced solid tumors and hepatic dysfunction: a National Cancer Institute Organ Dysfunction Working Group study
- PMID: 23653147
- PMCID: PMC3700623
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3214
Phase I study of pazopanib in patients with advanced solid tumors and hepatic dysfunction: a National Cancer Institute Organ Dysfunction Working Group study
Abstract
Purpose: Pazopanib is a potent, multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor; however, there is limited information regarding the effects of liver function on pazopanib metabolism and pharmacokinetics. The objective of this study was to establish the maximum-tolerated dose (MTD) and pharmacokinetic profile of pazopanib in patients with varying degrees of hepatic dysfunction.
Experimental design: Patients with any solid tumors or lymphoma were stratified into four groups based on the degree of hepatic dysfunction according to the National Cancer Institute Organ Dysfunction Working Group (NCI-ODWG) criteria. Pazopanib was given orally once a day on a 21-day cycle. A modified 3+3 design was used.
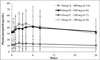
Results: Ninety-eight patients were enrolled. Patients in the mild group tolerated 800 mg per day. The moderate and severe groups tolerated 200 mg per day. Pharmacokinetic data in the mild group were similar to the data in the normal group. Comparison of the median Cmax and area under the curve [AUC(0-24)] in the moderate or severe groups at 200 mg per day to the values in the normal and mild groups at 800 mg per day indicated less than dose-proportional systemic exposures in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment. This suggests that the lower maximum-tolerated dose in the moderate and severe group is not due to a decrease in drug clearance or alteration in the proportion of metabolites.
Conclusions: In patients with mild liver dysfunction, pazopanib is well tolerated at the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved dose of 800 mg per day. Patients with moderate and severe liver dysfunction tolerated 200 mg per day.
©2013 AACR.
Figures
References
-
- Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J, Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J, et al. Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1061–1068. - PubMed
-
- Kumar R, Knick VB, Rudolph SK, Johnson JH, Crosby RM, Crouthamel MC, et al. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic correlation from mouse to human with pazopanib, a multikinase angiogenesis inhibitor with potent antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:2012–2021. - PubMed
-
- Hurwitz HI, Dowlati A, Saini S, Savage S, Suttle AB, Gibson DM, et al. Phase I trial of pazopanib in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:4220–4227. - PubMed
-
- Yau T, Chen PJ, Chan P, Curtis CM, Murphy PS, Suttle AB, et al. Phase I dose-finding study of pazopanib in hepatocellular carcinoma: evaluation of early efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:6914–6923. - PubMed
-
- GlaxoSmithKline RTP, NC 27709. Pazopanib. [package insert]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01-CA099168/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA069853/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-CA033572/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-CA006973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA166480/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-C062491/PHS HHS/United States
- U01-CA062505/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062490/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062505/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186691/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-CA062490/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062502/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186716/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062487/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA006973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-CA054174/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-CA069853/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062491/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-CA70095/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA070095/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-CA062502/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-CA062487/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA099168/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA054174/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA033572/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186717/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical