Rifaximin versus Nonabsorbable Disaccharides for the Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 23653636
- PMCID: PMC3638683
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/236963
Rifaximin versus Nonabsorbable Disaccharides for the Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
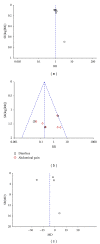
Background. Many studies have found that the antibiotic rifaximin is effective for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. However, there is no uniform view on the efficacy and safety of rifaximin. Methods. We performed a meta-analysis through electronic searches to evaluate the efficacy and safety of rifaximin in comparison with nonabsorbable disaccharides. Results. A total of 8 randomized controlled trials including 407 patients were included. The efficacy of rifaximin was equivalent to nonabsorbable disaccharides according to the statistical data (risk ratio (RR): 1.06, 95% CI: 0.94-1.19; P = 0.34). Analysis showed that patients treated with rifaximin had better results in serum ammonia levels (weighted mean difference (WMD): -10.63, 95% CI: -30.63-9.38; P = 0.30), mental status (WMD: -0.32, 95% CI: -0.67-0.03; P = 0.07), asterixis (WMD: -0.12, 95% CI: -0.31-0.08; P = 0.23), electroencephalogram response (WMD: -0.21, 95% CI: -0.34--0.09; P = 0.0007), and grades of portosystemic encephalopathy (WMD: -2.30, 95% CI: -2.78--1.82; P < 0.00001), but only the last ones had statistical significance. The safety of rifaximin was better than nonabsorbable disaccharides (RR: 0.19, 95% CI: 0.10-0.34; P < 0.00001). Conclusion. Rifaximin is at least as effective as nonabsorbable disaccharides, maybe better for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. And the safety of rifaximin is better.
Figures



References
-
- Bustamante J, Rimola A, Ventura PJ, et al. Prognostic significance of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Journal of Hepatology. 1999;30(5):890–895. - PubMed
-
- Garg H, Kumar A, Garg V, Sharma P, Sharma BC, Sarin SK. Clinical profile and predictors of mortality in patients of acute-on-chronic liver failure. Digestive and Liver Disease. 2012;44:166–171. - PubMed
-
- Abou-Assi S, Vlahcevic ZR. Hepatic encephalopathy: metabolic consequence of cirrhosis often is reversible. Postgraduate Medicine. 2001;109(2):52–65. - PubMed
-
- Stewart CA, Malinchoc M, Kim WR, Kamath PS. Hepatic encephalopathy as a predictor of survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Liver Transplantation. 2007;13(10):1366–1371. - PubMed
-
- Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, Tarter R, Weissenborn K, Blei AT. Hepatic encephalopathy—definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the Working Party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology. 2002;35(3):716–721. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

