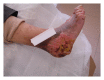
Verrucous carcinoma of the foot with bone invasion: a case report
- PMID: 23653876
- PMCID: PMC3638567
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/135307
Verrucous carcinoma of the foot with bone invasion: a case report
Abstract
Verrucous carcinoma of the foot often affects deep structures such as tendons, muscles, or bones. A 74-year-old man presented with a foot lesion that had been diagnosed as a skin infection 7 years earlier. He was treated with multiple excisions and superficial biopsies associated with antibiotic therapy without success. In our department he underwent an aggressive and accurate debridement with marginal excision harvesting multiple biopsies. Pathological evaluation of tissue at the time of operation confirmed the diagnosis of verrucous carcinoma of the foot. Therefore, the patient underwent an amputation below knee, and there were no postoperative complications; the patient was able to walk with the aid of a prosthesis with no signs of recurrence. The lesion follows a chronic course evolving from a discrete focal lesion to a large fungating deeply penetrating mass often compromised by local infection. The slow growth and confusing early-stage appearances can lead to delays in diagnosis of 8 to 15 years causing the extracutaneous involvement that requires a leg amputation. Many patients are initially treated with many topical medications without success, and most tumors have been treated as recalcitrant warts or corns for some time, whereas the basic approach is surgical.
Figures
References
-
- Dogan G, Oram Y, Hazneci E, Ozen S, Karincaoglu Y, Ciralik H. Three cases of verrucous carcinoma. Australasian Journal of Dermatology. 1998;39(4):251–254. - PubMed
-
- Green JG, Ferrara JA, Haber JA. Epithelioma cuniculatum plantare. Journal of Foot Surgery. 1987;26(1):78–83. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz RA. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosa. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 1995;32(1):1–24. - PubMed
-
- Ascione T, Iannece MD, Rosario P, et al. Impact of therapeutic choices on outcome of osteomyelitis caused by MRSA. Journal of Infection. 2011;63(1):102–104. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources