A case report and genetic characterization of a massive acinic cell carcinoma of the parotid with delayed distant metastases
- PMID: 23653877
- PMCID: PMC3638544
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/270362
A case report and genetic characterization of a massive acinic cell carcinoma of the parotid with delayed distant metastases
Abstract
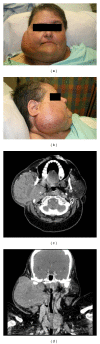
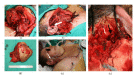
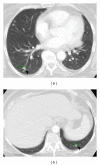
We describe the presentation, management, and clinical outcome of a massive acinic cell carcinoma of the parotid gland. The primary tumor and blood underwent exome sequencing which revealed deletions in CDKN2A as well as PPP1R13B, which induces p53. A damaging nonsynonymous mutation was noted in EP300, a histone acetylase which plays a role in cellular proliferation. This study provides the first insights into the genetic underpinnings of this cancer. Future large-scale efforts will be necessary to define the mutational landscape of salivary gland malignancies to identify therapeutic targets and biomarkers of treatment failure.
Figures

References
-
- SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2009. Bethesda, Md, USA: National Cancer Institute; 2012.
-
- Jessup JM, Menck HR, Winchester DP, Hundahl SA, Murphy GP. The National Cancer Data Base report on patterns of hospital reporting. Cancer. 1996;78:1829–1837. - PubMed
-
- Cesinaro AM, Criscuolo M, Collina G, Galetti R, Migaldi M, Lo Bianco F. Salivary gland tumors: revision of 391 cases according to the new WHO classification. Pathologica. 1994;86(6):602–605. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman HT, Karnell LH, Robinson RA, Pinkston JA, Menck HR. National Cancer Data Base report on cancer of the head and neck: acinic cell carcinoma. Head & Neck. 1999;21:297–309. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

