Anesthetic drug development: Novel drugs and new approaches
- PMID: 23653886
- PMCID: PMC3642742
- DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.109179
Anesthetic drug development: Novel drugs and new approaches
Abstract
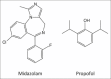
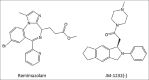
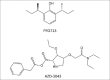
The ideal sedative-hypnotic drug would be a rapidly titratable intravenous agent with a high therapeutic index and minimal side effects. The current efforts to develop such agents are primarily focused on modifying the structures of existing drugs to improve their pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties. Drugs currently under development using this rational design approach include analogues of midazolam, propofol, and etomidate, such as remimazolam, PF0713, and cyclopropyl methoxycarbonyl-etomidate (MOC-etomidate), respectively. An alternative approach involves the rapid screening of large libraries of molecules for activity in structural or phenotypic assays that approximate anesthetic and target receptor interactions. Such high-throughput screening offers the potential for identifying completely novel classes of drugs. Anesthetic drug development is experiencing a resurgence of interest because there are new demands on our clinical practice that can be met, at least in part, with better agents. The goal of this review is to provide the reader with a glimpse of the novel anesthetic drugs and new developmental approaches that lie on the horizon.
Keywords: Anesthetic; etomidate; midazolam; propofol.
Figures
References
-
- Antonik LJ, Goldwater DR, Kilpatrick GJ, Tilbrook GS, Borkett KM. A Placebo-and midazolam-controlled, phase I, single ascending-dose study evaluating the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of remimazolam (CNS 7056): Part I. Safety, efficacy, and basic pharmacokinetics. Anesth Analg. 2012;115:274–83. - PubMed
-
- Bali M, Akabas MH. Defining the propofol binding site location on the GABAA receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;65:68–76. - PubMed
-
- Bennett SN, McNeil MM, Bland LA, Arduino MJ, Villarino ME, Perrotta DM, et al. Postoperative infections traced to contamination of an intravenous anesthetic, propofol. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:147–54. - PubMed
-
- Bodor N, Buchwald P. Soft drug design: General principles and recent applications. Med Res Rev. 2000;20:58–101. - PubMed
-
- Boulieu R, Lehmann B, Salord F, Fisher C, Morlet D. Pharmacokinetics of midazolam and its main metabolite 1-hydroxymidazolam in intensive care patients. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 1998;23:255–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

