On the acoustic effects of the supraglottic structures in excised larynges
- PMID: 23654402
- PMCID: PMC3663863
- DOI: 10.1121/1.4796109
On the acoustic effects of the supraglottic structures in excised larynges
Abstract
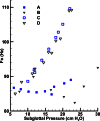
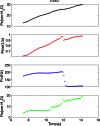
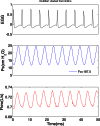
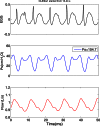
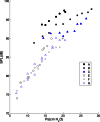
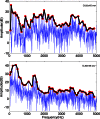
The acoustic effects of the supraglottic laryngeal structures (SGSs), including the false vocal folds (FVFs) laryngeal ventricle, and the epiglottis were investigated in an excised canine larynx model with and without these anatomical structures. The purpose of this study was to better understand the acoustic contributions of these structures to phonation. Canine larynges were prepared and mounted over a 3/4 in. tube, which supplied pressurized, heated, and humidified air. Glottal adduction was accomplished by rotating the arytenoids with a suture passed behind the vocal folds to simulate the lateral cricoarytenoid muscle action. The SGSs were kept intact in the first part of the experiment and were removed in the second part. Results indicated that when the FVFs vibrated, a low frequency component was observed in the spectral data. The excised larynx with a SGS had a limited range of frequency with subglottal pressure, while the larynx without a SGS had a larger frequency range. The excised canine larynx with a SGS oscillated with a higher phonation threshold pressure and significantly louder.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development of Excised Larynx.J Voice. 2020 Jan;34(1):38-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2018.07.023. Epub 2018 Sep 24. J Voice. 2020. PMID: 30262190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aerodynamic and acoustic effects of false vocal folds and epiglottis in excised larynx models.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2007 Feb;116(2):135-44. doi: 10.1177/000348940711600210. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2007. PMID: 17388238
-
Ventricular pressures in phonating excised larynges.J Acoust Soc Am. 2012 Aug;132(2):1017-26. doi: 10.1121/1.4730880. J Acoust Soc Am. 2012. PMID: 22894222 Free PMC article.
-
On pressure-frequency relations in the excised larynx.J Acoust Soc Am. 2007 Oct;122(4):2296-305. doi: 10.1121/1.2772230. J Acoust Soc Am. 2007. PMID: 17902865
-
[Functional anatomy of the larynx from clinical viewpoints. Part I: development, laryngeal skeleton, joints, insertion structures, musculature].HNO. 2007 Jul;55(7):583-98. doi: 10.1007/s00106-007-1556-2. HNO. 2007. PMID: 17431565 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Aerodynamic and acoustic effects of ventricular gap.J Voice. 2014 Mar;28(2):154-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2013.10.005. Epub 2013 Dec 8. J Voice. 2014. PMID: 24321590 Free PMC article.
-
Nonstimulated rabbit phonation model: Cricothyroid approximation.Laryngoscope. 2016 Jul;126(7):1589-94. doi: 10.1002/lary.25559. Epub 2016 Mar 12. Laryngoscope. 2016. PMID: 26971861 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Excised Larynx.J Voice. 2020 Jan;34(1):38-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2018.07.023. Epub 2018 Sep 24. J Voice. 2020. PMID: 30262190 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alipour, F., Jaiswal, S., and Finnegan, E. (2007). “ Aerodynamic and acoustic effects of false vocal folds and epiglottis in excised larynx models,” Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol 116, 135–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

