Flow cytometric assay detecting cytotoxicity against human endogenous retrovirus antigens expressed on cultured multiple sclerosis cells
- PMID: 23656307
- PMCID: PMC3949627
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12133
Flow cytometric assay detecting cytotoxicity against human endogenous retrovirus antigens expressed on cultured multiple sclerosis cells
Abstract
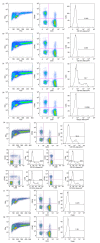
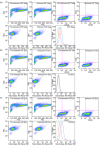
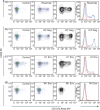
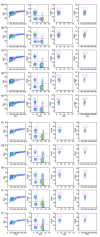
Damage of target cells by cytotoxicity, either mediated by specific lymphocytes or via antibody-dependent reactions, may play a decisive role in causing the central nervous system (CNS) lesions seen in multiple sclerosis (MS). Relevant epitopes, antibodies towards these epitopes and a reliable assay are all mandatory parts in detection and evaluation of the pertinence of such cytotoxicity reactions. We have adapted a flow cytometry assay detecting CD107a expression on the surface of cytotoxic effector cells to be applicable for analyses of the effect on target cells from MS patients expressing increased amounts of human endogenous retrovirus antigens. MS patients also have increased antibody levels to these antigens. The target cells are spontaneously growing peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of B cell lineage, expressing human endogenous retrovirus HERV epitopes on their surface. Polyclonal antibodies against defined peptides in the Env- and Gag-regions of the HERVs were raised in rabbits and used in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) -assays. Rituximab® (Roche), a chimeric monoclonal antibody against CD20 expressed primarily on B cells, was used as control antibody. Without antibodies this system is suitable for analyses of natural killer cell activity. In optimization of the assay we have used effector lymphocytes from healthy donors. The most effective effector cells are CD56(+) cells. CD8(+) T cells also express CD107a in ADCC. Using the adapted assay, we demonstrate significant ADCC activity to target cells expressing HERV epitopes, and additionally a low level of NK activity.
Keywords: ADCC; CD107a; HERV; NK cells; flow cytometry.
© 2013 British Society for Immunology.
Figures

References
-
- Bottley G, Cook GP, Blair GE. A flow cytometric assay for analysis of natural-killer cell-mediated cytolysis of adenovirus-transformed cells. Methods Mol Med. 2007;131:221–230. - PubMed
-
- Zimmermann SY, Esser R, Rohrbach E, Klingebiel T, Koehl U. A novel four-colour flow cytometric assay to determine natural killer cell or T-cell-mediated cellular cytotoxicity against leukaemic cells in peripheral or bone marrow specimens containing greater than 20% of normal cells. J Immunol Methods. 2005;296:63–76. - PubMed
-
- Cholujová D, Jakubíková J, Kubes M, et al. Comparative study of four fluorescent probes for evaluation of natural killer cell cytotoxicity assays. Immunobiology. 2008;213:629–640. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

