Oncogenic CSF3R mutations in chronic neutrophilic leukemia and atypical CML
- PMID: 23656643
- PMCID: PMC3730275
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1214514
Oncogenic CSF3R mutations in chronic neutrophilic leukemia and atypical CML
Abstract
Background: The molecular causes of many hematologic cancers remain unclear. Among these cancers are chronic neutrophilic leukemia (CNL) and atypical (BCR-ABL1-negative) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), both of which are diagnosed on the basis of neoplastic expansion of granulocytic cells and exclusion of genetic drivers that are known to occur in other myeloproliferative neoplasms and myeloproliferative-myelodysplastic overlap neoplasms.
Methods: To identify potential genetic drivers in these disorders, we used an integrated approach of deep sequencing coupled with the screening of primary leukemia cells obtained from patients with CNL or atypical CML against panels of tyrosine kinase-specific small interfering RNAs or small-molecule kinase inhibitors. We validated candidate oncogenes using in vitro transformation assays, and drug sensitivities were validated with the use of assays of primary-cell colonies.
Results: We identified activating mutations in the gene encoding the receptor for colony-stimulating factor 3 (CSF3R) in 16 of 27 patients (59%) with CNL or atypical CML. These mutations segregate within two distinct regions of CSF3R and lead to preferential downstream kinase signaling through SRC family-TNK2 or JAK kinases and differential sensitivity to kinase inhibitors. A patient with CNL carrying a JAK-activating CSF3R mutation had marked clinical improvement after the administration of the JAK1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib.
Conclusions: Mutations in CSF3R are common in patients with CNL or atypical CML and represent a potentially useful criterion for diagnosing these neoplasms. (Funded by the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society and others.).
Figures
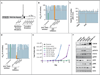
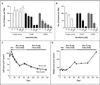

Comment in
-
Genetically informed therapy in leukemia.N Engl J Med. 2013 May 9;368(19):1838-9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1302363. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 23656651 No abstract available.
References
-
- Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2408–2417. - PubMed
-
- Krause DS, Van Etten RA. Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:172–187. - PubMed
-
- Bain BJ, Brunning RD, Vardiman JW, Thiele J. Chronic neutrophilic leukaemia. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Lee Harris N, et al., editors. WHO classification of tumors of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2008. pp. 38–39.
-
- Vardiman JW, Bennett JM, Bain BJ, Brunning RD, Thiele J. Atypical chronic myeloid leukaemia, BCR-ABL1 negative. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Lee Harris N, et al., editors. WHO classification of tumors of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2008. pp. 80–81.
-
- Froberg MK, Brunning RD, Dorion P, Litz CE, Torlakovic E. Demonstration of clonality in neutrophils using FISH in a case of chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Leukemia. 1998;12:623–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 HL106576/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007781/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 4 R00CA151457-03/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA151457/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30CA069533-13/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM071338/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1-K99-CA151670-01A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K99 CA151670/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- 5T32HL007781-20/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA069533/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5UL1RR024140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
