Molecular and structural insight into lysine selection on substrate and ubiquitin lysine 48 by the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Cdc34
- PMID: 23656784
- PMCID: PMC3713132
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.24818
Molecular and structural insight into lysine selection on substrate and ubiquitin lysine 48 by the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Cdc34
Abstract
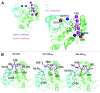
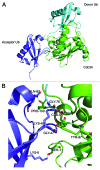
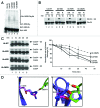
The attachment of ubiquitin (Ub) to lysines on substrates or itself by ubiquitin-conjugating (E2) and ubiquitin ligase (E3) enzymes results in protein ubiquitination. Lysine selection is important for generating diverse substrate-Ub structures and targeting proteins to different fates; however, the mechanisms of lysine selection are not clearly understood. The positioning of lysine(s) toward the E2/E3 active site and residues proximal to lysines are critical in their selection. We investigated determinants of lysine specificity of the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Cdc34, toward substrate and Ub lysines. Evaluation of the relative importance of different residues positioned -2, -1, +1 and +2 toward ubiquitination of its substrate, Sic1, on lysine 50 showed that charged residues in the -1 and -2 positions negatively impact on ubiquitination. Modeling suggests that charged residues at these positions alter the native salt-bridge interactions in Ub and Cdc34, resulting in misplacement of Sic1 lysine 50 in the Cdc34 catalytic cleft. During polyubiquitination, Cdc34 showed a strong preference for Ub lysine 48 (K48), with lower activity towards lysine 11 (K11) and lysine 63 (K63). Mutating the -2, -1, +1 and +2 sites surrounding K11 and K63 to mimic those surrounding K48 did not improve their ubiquitination, indicating that further determinants are important for Ub K48 specificity. Modeling the ternary structure of acceptor Ub with the Cdc34~Ub complex as well as in vitro ubiquitination assays unveiled the importance of K6 and Q62 of acceptor Ub for Ub K48 polyubiquitination. These findings provide molecular and structural insight into substrate lysine and Ub K48 specificity by Cdc34.
Keywords: Cdc34; SCF; Sic1; cell cycle; lysine; ubiquitin.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
