Pharmacological and genetical evidence supporting nitric oxide requirement for 2,4-epibrassinolide regulation of root architecture in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 23656880
- PMCID: PMC3908936
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.24712
Pharmacological and genetical evidence supporting nitric oxide requirement for 2,4-epibrassinolide regulation of root architecture in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
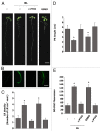
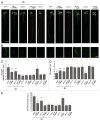
Brassinosteroids (BRs) regulate various physiological processes, such as tolerance to stresses and root growth. Recently, a connection was reported between BRs and nitric oxide (NO) in plant responses to abiotic stress. Here we present evidence supporting NO functions in BR signaling during root growth process. Arabidopsis seedlings treated with BR 24-epibrassinolide (BL) show increased lateral roots (LR) density, inhibition of primary root (PR) elongation and NO accumulation. Similar effects were observed adding the NO donor GSNO to BR-receptor mutant bri1-1. Furthermore, BL-induced responses in the root were abolished by the specific NO scavenger c-PTIO. The activities of nitrate reductase (NR) and nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-like, two NO generating enzymes were involved in BR signaling. These results demonstrate that BR increases the NO concentration in root cells, which is required for BR-induced changes in root architecture.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; brassinosteroids; nitric oxide; root morphology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide is involved in the brassinolide-induced adventitious root development in cucumber.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Mar 6;20(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-2320-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32138654 Free PMC article.
-
Brassinosteroids Mitigate Cadmium Effects in Arabidopsis Root System without Any Cooperation with Nitric Oxide.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 13;23(2):825. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020825. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35055009 Free PMC article.
-
A mathematical model for BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE1-mediated signaling in root growth and hypocotyl elongation.Plant Physiol. 2012 Sep;160(1):523-32. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.200105. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22802611 Free PMC article.
-
Review: Emerging roles of brassinosteroid in nutrient foraging.Plant Sci. 2020 Jul;296:110474. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110474. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32540004 Review.
-
Brassinosteroid signaling in plant development and adaptation to stress.Development. 2019 Mar 14;146(5):dev151894. doi: 10.1242/dev.151894. Development. 2019. PMID: 30872266 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nitric oxide and phytohormone interactions: current status and perspectives.Front Plant Sci. 2013 Oct 9;4:398. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00398. Front Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 24130567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of NO-Generating System Activity in Cucumber Root Response to Cold.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 13;26(4):1599. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041599. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004064 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-tuned nitric oxide and hormone interface in plant root development and regeneration.J Exp Bot. 2023 Oct 13;74(19):6104-6118. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac508. J Exp Bot. 2023. PMID: 36548145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitric oxide signaling and its crosstalk with other plant growth regulators in plant responses to abiotic stress.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Jan;24(3):2273-2285. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7947-8. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 27812964 Review.
-
Nitric oxide is involved in the brassinolide-induced adventitious root development in cucumber.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Mar 6;20(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-2320-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32138654 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
