The ChEMBL database as linked open data
- PMID: 23657106
- PMCID: PMC3700754
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-2946-5-23
The ChEMBL database as linked open data
Abstract
Background: Making data available as Linked Data using Resource Description Framework (RDF) promotes integration with other web resources. RDF documents can natively link to related data, and others can link back using Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs). RDF makes the data machine-readable and uses extensible vocabularies for additional information, making it easier to scale up inference and data analysis.
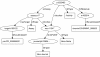
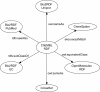
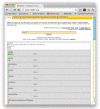
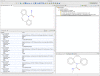
Results: This paper describes recent developments in an ongoing project converting data from the ChEMBL database into RDF triples. Relative to earlier versions, this updated version of ChEMBL-RDF uses recently introduced ontologies, including CHEMINF and CiTO; exposes more information from the database; and is now available as dereferencable, linked data. To demonstrate these new features, we present novel use cases showing further integration with other web resources, including Bio2RDF, Chem2Bio2RDF, and ChemSpider, and showing the use of standard ontologies for querying.
Conclusions: We have illustrated the advantages of using open standards and ontologies to link the ChEMBL database to other databases. Using those links and the knowledge encoded in standards and ontologies, the ChEMBL-RDF resource creates a foundation for integrated semantic web cheminformatics applications, such as the presented decision support.
Figures
References
-
- Staab CA, Ceder R, Jägerbrink T, Nilsson JA, Roberg K, Jörnvall H, Höög JO, Grafström RC. Bioinformatics processing of protein and transcript profiles of normal and transformed cell lines indicates functional impairment of transcriptional regulators in Buccal Carcinoma. J Proteome Res. 2007;5(9):3705–3717. doi: 10.1021/pr070308q. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Williams AJ, Harland L, Groth P, Pettifer S, Chichester C, Willighagen EL, Evelo CT, Blomberg N, Ecker G, Goble C, Mons B. Open PHACTS: semantic interoperability for drug discovery. Drug Discov Today. 2012;5(21–22) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

