IQGAP1 links PDGF receptor-β signal to focal adhesions involved in vascular smooth muscle cell migration: role in neointimal formation after vascular injury
- PMID: 23657573
- PMCID: PMC3761176
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00011.2013
IQGAP1 links PDGF receptor-β signal to focal adhesions involved in vascular smooth muscle cell migration: role in neointimal formation after vascular injury
Abstract
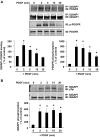
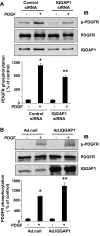
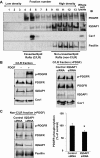
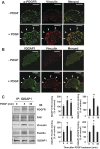
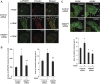
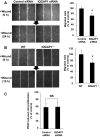
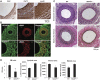
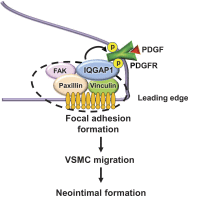
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) migration and neointimal formation in response to injury. We previously identified IQ-domain GTPase-activating protein 1 (IQGAP1) as a novel VEGF receptor 2 binding scaffold protein involved in endothelial migration. However, its role in VSMC migration and neointimal formation in vivo is unknown. Here we show that PDGF stimulation rapidly promotes IQGAP1 association with PDGF receptor-β (PDGFR) as well as IQGAP1 tyrosine phosphorylation in cultured VSMC. Overexpression or knockdown of IQGAP1 enhances or inhibits PDGFR autophosphorylation (p-PDGFR), respectively. Immunofluorescence and cell fractionation analysis reveals that PDGF-induced p-PDGFR localized in focal adhesions (FAs), but not caveolae/lipid rafts, is inhibited by IQGAP1 knockdown with siRNA. PDGF stimulation promotes IQGAP1 association with PDGFR/FA signaling protein complex. Functionally, IQGAP1 siRNA inhibits PDGF-induced FA formation as well as VSMC migration induced by PDGF. In vivo, IQGAP1 expression is markedly increased at neointimal VSMC in wire-injured femoral arteries. Mice lacking IQGAP1 exhibit impaired neointimal formation in response to vascular injury. In summary, IQGAP1, through interaction with PDGFR and FA signaling proteins, promotes activation of PDGFR in FAs as well as FA formation, which may contribute to VSMC migration and neointimal formation after injury. Our findings provide insight into IQGAP1 as a potential therapeutic target for vascular migration-related diseases.
Keywords: IQGAP1; migration; platelet-derived growth factor; vascular injury; vascular smooth muscle cell.
Figures
References
-
- Autieri MV. Increasing our IQ of vascular smooth muscle cell migration with IQGAP1. Focus on “IQGAP1 links PDGF receptor-β signal to focal adhesions involved in vascular smooth muscle cell migration: role in neointimal formation after vascular injury.” Am J Physiol Cell Physiol (May 8, 2013). 10.1152/ajpcell.00125.2013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bensenor LB, Kan HM, Wang N, Wallrabe H, Davidson LA, Cai Y, Schafer DA, Bloom GS. IQGAP1 regulates cell motility by linking growth factor signaling to actin assembly. J Cell Sci 120: 658–669, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Brown MD, Sacks DB. IQGAP1 in cellular signaling: bridging the GAP. Trends Cell Biol 16: 242–249, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

