Nonspecific, reversible inhibition of voltage-gated calcium channels by CaMKII inhibitor CK59
- PMID: 23657616
- PMCID: PMC3693846
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-013-9941-8
Nonspecific, reversible inhibition of voltage-gated calcium channels by CaMKII inhibitor CK59
Abstract
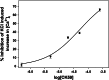
Investigation of kinase-related processes often uses pharmacological inhibition to reveal pathways in which kinases are involved. However, one concern about using such kinase inhibitors is their potential lack of specificity. Here, we report that the calcium-calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) inhibitor CK59 inhibited multiple voltage-gated calcium channels, including the L-type channel during depolarization in a dose-dependent manner. The use of another CaMKII inhibitor, cell-permeable autocamtide-2 related inhibitory peptide II (Ant-AIP-II), failed to similarly decrease calcium current or entry in hippocampal cultures, as shown by ratiometric calcium imaging and whole-cell patch clamp electrophysiology. Notably, inhibition due to CK59 was reversible; washout of the drug brought calcium levels back to control values upon depolarization. Furthermore, the IC50 for CK59 was approximately 50 μM, which is only fivefold larger than the reported IC50 values for CaMKII inhibition. Similar nonspecific actions of other CaMKII inhibitors KN93 and KN62 have previously been reported. In the case of all three kinase inhibitors, the IC50 for calcium current inhibition falls near that of CaMKII inhibition. Our findings demonstrate that CK59 attenuates activity of voltage-gated calcium channels, and thus provide more evidence for caution when relying on pharmacological inhibition to examine kinase-dependent phenomena.
Figures



References
-
- Carter TJ, Mynlieff M (2004) Gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptors facilitate L-type and attenuate N-type Ca(2+) currents in isolated hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Res 76:323–333 - PubMed
-
- Castelli L, Magistretti J (2006) High-voltage-activated Ca2+ currents show similar patterns of expression in stellate and pyramidal cells from rat entorhinal cortex layer II. Brain Res 1090:76–88 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

