Chemoattractant stimulation of TORC2 is regulated by receptor/G protein-targeted inhibitory mechanisms that function upstream and independently of an essential GEF/Ras activation pathway in Dictyostelium
- PMID: 23657816
- PMCID: PMC3694798
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E13-03-0130
Chemoattractant stimulation of TORC2 is regulated by receptor/G protein-targeted inhibitory mechanisms that function upstream and independently of an essential GEF/Ras activation pathway in Dictyostelium
Abstract
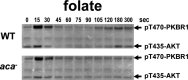
Global stimulation of Dictyostelium with different chemoattractants elicits multiple transient signaling responses, including synthesis of cAMP and cGMP, actin polymerization, activation of kinases ERK2, TORC2, and phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase, and Ras-GTP accumulation. Mechanisms that down-regulate these responses are poorly understood. Here we examine transient activation of TORC2 in response to chemically distinct chemoattractants, cAMP and folate, and suggest that TORC2 is regulated by adaptive, desensitizing responses to stimulatory ligands that are independent of downstream, feedback, or feedforward circuits. Cells with acquired insensitivity to either folate or cAMP remain fully responsive to TORC2 activation if stimulated with the other ligand. Thus TORC2 responses to cAMP or folate are not cross-inhibitory. Using a series of signaling mutants, we show that folate and cAMP activate TORC2 through an identical GEF/Ras pathway but separate receptors and G protein couplings. Because the common GEF/Ras pathway also remains fully responsive to one chemoattractant after desensitization to the other, GEF/Ras must act downstream and independent of adaptation to persistent ligand stimulation. When initial chemoattractant concentrations are immediately diluted, cells rapidly regain full responsiveness. We suggest that ligand adaptation functions in upstream inhibitory pathways that involve chemoattractant-specific receptor/G protein complexes and regulate multiple response pathways.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of chemoattractant receptors regulates chemotaxis, actin reorganization and signal relay.J Cell Sci. 2013 Oct 15;126(Pt 20):4614-26. doi: 10.1242/jcs.122952. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23902692 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase A regulates the Ras, Rap1 and TORC2 pathways in response to the chemoattractant cAMP in Dictyostelium.J Cell Sci. 2017 May 1;130(9):1545-1558. doi: 10.1242/jcs.177170. Epub 2017 Mar 16. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28302905 Free PMC article.
-
A novel Ras-interacting protein required for chemotaxis and cyclic adenosine monophosphate signal relay in Dictyostelium.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Sep;10(9):2829-45. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.9.2829. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10473630 Free PMC article.
-
G-Protein Dependent Signal Transduction and Ubiquitination in Dictyostelium.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Oct 19;18(10):2180. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102180. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29048338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function and Regulation of Heterotrimeric G Proteins during Chemotaxis.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jan 14;17(1):90. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010090. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26784171 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CRISPR-mediated reversion of oncogenic KRAS mutation results in increased proliferation and reveals independent roles of Ras and mTORC2 in the migration of A549 lung cancer cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2023 Dec 1;34(13):ar128. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-05-0152. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2023. PMID: 37729017 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of Live Bacterial Sensing for Chemotaxis and Phagocytosis and of Macropinocytosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Mar 2;8:62. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00062. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29552545 Free PMC article.
-
Dual TORCs driven and B56 orchestrated signaling network guides eukaryotic cell migration.BMB Rep. 2017 Sep;50(9):437-444. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.9.091. BMB Rep. 2017. PMID: 28571594 Free PMC article.
-
Forty-five years of cGMP research in Dictyostelium: understanding the regulation and function of the cGMP pathway for cell movement and chemotaxis.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Oct 1;32(20):ar8. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-04-0171. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34347507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolutionarily conserved coupling of adaptive and excitable networks mediates eukaryotic chemotaxis.Nat Commun. 2014 Oct 27;5:5175. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6175. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25346418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chakrabarti S, Regec A, Gintzler AR. Chronic morphine acts via a protein kinase C(gamma)-G(beta)-adenylyl cyclase complex to augment phosphorylation of G(beta) and G(betagamma) stimulatory adenylyl cyclase signaling. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005;138:94–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

