Memory decay and susceptibility to amnesia dissociate punishment--from relief-learning
- PMID: 23658002
- PMCID: PMC3730614
- DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2012.1171
Memory decay and susceptibility to amnesia dissociate punishment--from relief-learning
Abstract
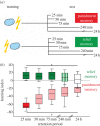
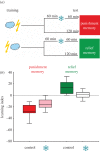
Painful events shape future behaviour in two ways: stimuli associated with pain onset subsequently support learned avoidance (i.e. punishment-learning) because they signal future, upcoming pain. Stimuli associated with pain offset in turn signal relief and later on support learned approach (i.e. relief-learning). The relative strengths of such punishment- and relief-learning can be crucial for the adaptive organization of behaviour in the aftermath of painful events. Using Drosophila, we compare punishment- and relief-memories in terms of their temporal decay and sensitivity to retrograde amnesia. During the first 75 min following training, relief-memory is stable, whereas punishment-memory decays to half of the initial score. By 24 h after training, however, relief-memory is lost, whereas a third of punishment-memory scores still remain. In accordance with such rapid temporal decay from 75 min on, retrograde amnesia erases relief-memory but leaves a half of punishment-memory scores intact. These findings suggest differential mechanistic bases for punishment- and relief-memory, thus offering possibilities for separately interfering with either of them.
Keywords: Drosophila melanogaster; memory stability; punishment-learning; reinforcement; relief-learning; retrograde amnesia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pain-relief learning in flies, rats, and man: basic research and applied perspectives.Learn Mem. 2014 Mar 18;21(4):232-52. doi: 10.1101/lm.032995.113. Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24643725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synapsin determines memory strength after punishment- and relief-learning.J Neurosci. 2015 May 13;35(19):7487-502. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4454-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25972175 Free PMC article.
-
Reinforcement signaling of punishment versus relief in fruit flies.Learn Mem. 2018 May 15;25(6):247-257. doi: 10.1101/lm.047308.118. Print 2018 Jun. Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 29764970 Free PMC article.
-
Independent natural genetic variation of punishment- versus relief-memory.Biol Lett. 2016 Dec;12(12):20160657. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2016.0657. Biol Lett. 2016. PMID: 28003518 Free PMC article.
-
Maggot learning and Synapsin function.J Exp Biol. 2013 Mar 15;216(Pt 6):939-51. doi: 10.1242/jeb.076208. J Exp Biol. 2013. PMID: 23447663 Review.
Cited by
-
Differences in long-term memory stability and AmCREB level between forward and backward conditioned honeybees (Apis mellifera).Front Behav Neurosci. 2015 Apr 27;9:91. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00091. eCollection 2015. Front Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25964749 Free PMC article.
-
Pain-relief learning in flies, rats, and man: basic research and applied perspectives.Learn Mem. 2014 Mar 18;21(4):232-52. doi: 10.1101/lm.032995.113. Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24643725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synapsin determines memory strength after punishment- and relief-learning.J Neurosci. 2015 May 13;35(19):7487-502. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4454-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25972175 Free PMC article.
-
Reinforcement signaling of punishment versus relief in fruit flies.Learn Mem. 2018 May 15;25(6):247-257. doi: 10.1101/lm.047308.118. Print 2018 Jun. Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 29764970 Free PMC article.
-
Independent natural genetic variation of punishment- versus relief-memory.Biol Lett. 2016 Dec;12(12):20160657. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2016.0657. Biol Lett. 2016. PMID: 28003518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Solomon RL, Corbit JD. 1974. An opponent-process theory of motivation. I. Temporal dynamics of affect. Psychol. Rev. 81, 119–14510.1037/h0036128 (doi:10.1037/h0036128) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tanimoto H, Heisenberg M, Gerber B. 2004. Event timing turns punishment to reward. Nature 430, 983.10.1038/430983a (doi:10.1038/430983a) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yarali A, Niewalda T, Chen Y, Tanimoto H, Duerrnagel S, Gerber B. 2008. Pain relief-learning in fruit flies. Anim. Behav. 76, 1173–118510.1016/j.anbehav.2008.05.025 (doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2008.05.025) - DOI - DOI
-
- Andreatta M, Mühlberger A, Yarali A, Gerber B, Pauli P. 2010. A rift between implicit and explicit conditioned valence in human pain relief-learning. Proc. R. Soc. B 277, 2411–241610.1098/rspb.2010.0103 (doi:10.1098/rspb.2010.0103) - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andreatta M, Fendt M, Mühlberger A, Wieser MJ, Imobersteg S, Yarali A, Gerber B, Pauli P. 2012. Onset and offset of aversive events establish distinct memories requiring fear- and reward networks. Learn. Mem. 19, 518–52610.1101/lm.026864.112 (doi:10.1101/lm.026864.112) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

