In vivo stimulus-induced vasodilation occurs without IP3 receptor activation and may precede astrocytic calcium increase
- PMID: 23658179
- PMCID: PMC3712855
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3285-12.2013
In vivo stimulus-induced vasodilation occurs without IP3 receptor activation and may precede astrocytic calcium increase
Abstract
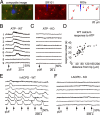
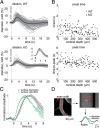
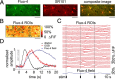
Calcium-dependent release of vasoactive gliotransmitters is widely assumed to trigger vasodilation associated with rapid increases in neuronal activity. Inconsistent with this hypothesis, intact stimulus-induced vasodilation was observed in inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) type-2 receptor (R2) knock-out (KO) mice, in which the primary mechanism of astrocytic calcium increase-the release of calcium from intracellular stores following activation of an IP3-dependent pathway-is lacking. Further, our results in wild-type (WT) mice indicate that in vivo onset of astrocytic calcium increase in response to sensory stimulus could be considerably delayed relative to the simultaneously measured onset of arteriolar dilation. Delayed calcium increases in WT mice were observed in both astrocytic cell bodies and perivascular endfeet. Thus, astrocytes may not play a role in the initiation of blood flow response, at least not via calcium-dependent mechanisms. Moreover, an increase in astrocytic intracellular calcium was not required for normal vasodilation in the IP3R2-KO animals.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS051188/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- EB009118/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL080101/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS054736/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR029050/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057198/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- EB00790/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- NS055104/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS055104/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB009118/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- NS051188/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007198/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057476/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000790/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- NS057476/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS054736/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS057198/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
