Critical role of a survivin/TGF-β/mTORC1 axis in IGF-I-mediated growth of prostate epithelial cells
- PMID: 23658701
- PMCID: PMC3641055
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061896
Critical role of a survivin/TGF-β/mTORC1 axis in IGF-I-mediated growth of prostate epithelial cells
Abstract
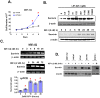
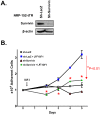
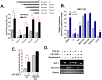
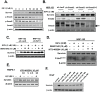
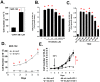
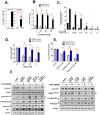
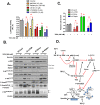
Survivin is a unique member of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) proteins that is overexpressed in numerous cancers through poorly defined mechanisms. One such mechanism may be through constitutive activation of the insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) signaling pathway, implicated in the development and progression of prostate cancer. Using the pre-neoplastic NRP-152 rat prostate cell line as a model, we showed that IGF-I induces Survivin expression, and that silencing Survivin by lentiviral-mediated small hairpin RNA (shRNA) represses IGF-I-stimulated cell growth, implicating Survivin as a mediator of this growth response. Moreover, our data support that the induction of Survivin by IGF-I occurs through a transcriptional mechanism that is mediated in part by the PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 pathway. Use of various Survivin promoter-luciferase constructs revealed that the CDE and CHR response elements in the proximal region of the Survivin promoter are involved in this IGF-I response. Transforming growth factor (TGF-β) signaling antagonists similarly activated the Surivin promoter and rendered cells refractory to further promoter activation by IGF-I. IGF-I suppressed levels of phospho-Smads 2 and 3 with kinetics similar to that of Survivin induction. Suppression of TGF-β signaling, either by TGF-β receptor kinase inhibitors or by silencing Smads 2 and 3, induced Survivin expression and promoted cell growth similar to that induced by IGF-I. TGF-β receptor antagonists also rescued cells from down-regulation of Survivin expression and growth suppression by pharmacological inhibitors of PI3K, Akt, MEK and mTOR. Sh-RNA gene silencing studies suggest that mTORC1 induces while mTORC2 represses the expression of Survivin by IGF-I. Taken together, these results suggest that IGF-I signaling through a PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 mechanism elevates expression of Survivin and promotes growth of prostate epithelial cells by suppressing Smad-dependent autocrine TGF-β signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Liston P, Fong WG, Korneluk RG (2003) The inhibitors of apoptosis: there is more to life than Bcl2. Oncogene 22: 8568–8580. - PubMed
-
- Salvesen GS, Duckett CS (2002) IAP proteins: blocking the road to death's door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 401–410. - PubMed
-
- Dohi T, Okada K, Xia F, Wilford CE, Samuel T, et al. (2004) An IAP-IAP complex inhibits apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279: 34087–34090. - PubMed
-
- Song Z, Yao X, Wu M (2003) Direct interaction between survivin and Smac/DIABLO is essential for the anti-apoptotic activity of survivin during taxol-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 278: 23130–23140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

