Protein expression of ZEB2 in renal cell carcinoma and its prognostic significance in patient survival
- PMID: 23658743
- PMCID: PMC3642198
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062558
Protein expression of ZEB2 in renal cell carcinoma and its prognostic significance in patient survival
Abstract
Background: ZEB2 has been reportedly shown to mediate the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and disease aggressiveness in human tumors. However, the expression status of ZEB2 in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and ZEB2's clinicopathologic/prognostic significance are poorly understood.
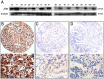
Methodology/principal findings: In this study, tissue microarray, immunohistochemistry (IHC) and western blot analyses were utilized to investigate the ZEB2 expression status in RCC and adjacent renal tissue samples. In our study, samples from 116 RCC patients treated with radical nephrectomy were used as a training set to generate a ZEB2 optimal cut-point for patient outcome by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. For validation, the correlation of ZEB2 expression with the clinical characteristics and patient outcomes in another set (including 113 patients) was analyzed to validate the obtained cut-point. In the training and validation sets, high expression of ZEB2, defined by ROC analysis, predicted a poorer overall survival and progression-free survival, as evidenced by the univariate and multivariate analyses. In different subsets of overall patients, ZEB2 expression was also a prognostic indicator in patients with stage I/II, stage III/IV, grade 1/2 and grade 3/4 disease (P<0.05). Downregulation of ZEB2 by shRNA decreased the migration and invasion ability of 769-P cells in vitro. Furthermore, high ZEB2 expression was positively correlated with vimentin expression and inversely linked to E-cadherin expression in RCC.
Conclusions/significance: Our findings provide a basis for the concept that high ZEB2 expression in RCC may be important in the acquisition of an aggressive phenotype. This evidence suggests that ZEB2 overexpression (examined by IHC) is an independent biomarker for the poor prognosis of patients with RCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A (2011) Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin 61: 212–236. - PubMed
-
- (2008) Cancer incidence in five continents. Volume IX. IARC Sci Publ: 1–837. - PubMed
-
- Lam JS, Breda A, Belldegrun AS, Figlin RA (2006) Evolving principles of surgical management and prognostic factors for outcome in renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 24: 5565–5575. - PubMed
-
- Kim SP, Alt AL, Weight CJ, Costello BA, Cheville JC, et al. (2011) Independent validation of the 2010 American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM classification for renal cell carcinoma: results from a large, single institution cohort. J Urol 185: 2035–2039. - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Weinberg RA (2008) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: at the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell 14: 818–829. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

