Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced resistance to doxorubicin is reversed by paeonol treatment in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 23658755
- PMCID: PMC3643935
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062627
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced resistance to doxorubicin is reversed by paeonol treatment in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract
Background: Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress) is generally activated in solid tumors and results in tumor cell anti-apoptosis and drug resistance. Paeonol (Pae, 2-hydroxy-4-methoxyacetophenone), is a natural product extracted from the root of Paeonia Suffruticosa Andrew. Although Pae displays anti-neoplastic activity and increases the efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs in various cell lines and in animal models, studies related to the effect of Pae on ER stress-induced resistance to chemotherapeutic agents in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are poorly understood.
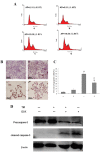
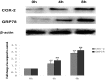
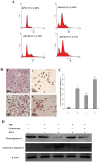
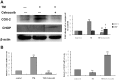
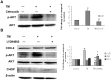
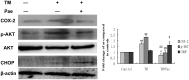
Methodology/principal findings: In this study, we investigated the effect of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response during resistance of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to doxorubicin. Treatment with the ER stress-inducer tunicamycin (TM) before the addition of doxorubicin reduced the rate of apoptosis induced by doxorubicin. Interestingly, co-pretreatment with tunicamycin and Pae significantly increased apoptosis induced by doxorubicin. Furthermore, induction of ER stress resulted in increasing expression of COX-2 concomitant with inactivation of Akt and up-regulation of the pro-apoptotic transcription factor CHOP (GADD153) in HepG2 cells. These cellular changes in gene expression and Akt activation may be an important resistance mechanism against doxorubicin in hepatocellular carcinoma cells undergoing ER stress. However, co-pretreatment with tunicamycin and Pae decreased the expression of COX-2 and levels of activation of Akt as well as increasing the levels of CHOP in HCC cells.
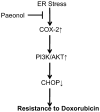
Conclusions/significance: Our results demonstrate that Pae reverses ER stress-induced resistance to doxorubicin in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting COX-2 mediated inactivation of PI3K/AKT/CHOP.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Lencioni R, Chen XP, Dagher L, Venook AP (2010) Treatment of intermediate/advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in the clinic: how can outcomes be improved? Oncologist 15 Suppl 442–52. - PubMed
-
- Mendizabal M, Reddy KR (2009) Current management of hepatocellular carcinoma.Med Clin North Am 93:885–900, viii. - PubMed
-
- Kapoor A, Sanyal AJ (2009) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response.Clin Liver Dis. 13: 581–590. - PubMed
-
- Rasheva VI, Domingos PM (2009) Cellular responses to endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Apoptosis 14: 996–1007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

