The connection of monocytes and reactive oxygen species in pain
- PMID: 23658840
- PMCID: PMC3642180
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063564
The connection of monocytes and reactive oxygen species in pain
Abstract
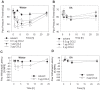
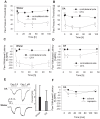
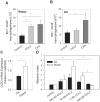
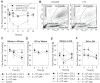
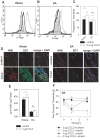
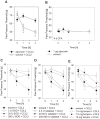
The interplay of specific leukocyte subpopulations, resident cells and proalgesic mediators results in pain in inflammation. Proalgesic mediators like reactive oxygen species (ROS) and downstream products elicit pain by stimulation of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels. The contribution of leukocyte subpopulations however is less clear. Local injection of neutrophilic chemokines elicits neutrophil recruitment but no hyperalgesia in rats. In meta-analyses the monocytic chemoattractant, CCL2 (monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; MCP-1), was identified as an important factor in the pathophysiology of human and animal pain. In this study, intraplantar injection of CCL2 elicited thermal and mechanical pain in Wistar but not in Dark Agouti (DA) rats, which lack p47(phox), a part of the NADPH oxidase complex. Inflammatory hyperalgesia after complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) as well as capsaicin-induced hyperalgesia and capsaicin-induced current flow in dorsal root ganglion neurons in DA were comparable to Wistar rats. Macrophages from DA expressed lower levels of CCR2 and thereby migrated less towards CCL2 and formed limited amounts of ROS in vitro and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) in the tissue in response to CCL2 compared to Wistar rats. Local adoptive transfer of peritoneal macrophages from Wistar but not from DA rats reconstituted CCL2-triggered hyperalgesia in leukocyte-depleted DA and Wistar rats. A pharmacological stimulator of ROS production (phytol) restored CCL2-induced hyperalgesia in vivo in DA rats. In Wistar rats, CCL2-induced hyperalgesia was completely blocked by superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase or tempol. Likewise, inhibition of NADPH oxidase by apocynin reduced CCL2-elicited hyperalgesia but not CFA-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia. In summary, we provide a link between CCL2, CCR2 expression on macrophages, NADPH oxidase, ROS and the development CCL2-triggered hyperalgesia, which is different from CFA-induced hyperalgesia. The study further supports the impact of CCL2 and ROS as potential targets in pain therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The molecular link between C-C-chemokine ligand 2-induced leukocyte recruitment and hyperalgesia.J Pain. 2013 Sep;14(9):897-910. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2013.02.012. Epub 2013 May 16. J Pain. 2013. PMID: 23683582
-
Mechanistic insights into the role of the chemokine CCL2/CCR2 axis in dorsal root ganglia to peripheral inflammation and pain hypersensitivity.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Mar 23;18(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02125-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 33757529 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced oxidation protein products sensitized the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 via NADPH oxidase 1 and 4 to cause mechanical hyperalgesia.Redox Biol. 2016 Dec;10:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Sep 17. Redox Biol. 2016. PMID: 27665186 Free PMC article.
-
A brief look at the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (CCL2) in the pathophysiology of psoriasis.Cytokine. 2018 Oct;110:226-231. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.12.010. Epub 2017 Dec 23. Cytokine. 2018. PMID: 29277337 Review.
-
Nitroxidative Signaling Mechanisms in Pathological Pain.Trends Neurosci. 2016 Dec;39(12):862-879. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2016.10.003. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Trends Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27842920 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of antioxidant supplementation on dysmenorrhea and endometriosis-associated painful symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2024 Mar;67(2):186-198. doi: 10.5468/ogs.23210. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38221738 Free PMC article.
-
Bipolar disorder: role of immune-inflammatory cytokines, oxidative and nitrosative stress and tryptophan catabolites.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2015 Feb;17(2):8. doi: 10.1007/s11920-014-0541-1. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2015. PMID: 25620790 Review.
-
Regulatory T Cells and Their Derived Cytokine, Interleukin-35, Reduce Pain in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.J Neurosci. 2019 Mar 20;39(12):2326-2346. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1815-18.2019. Epub 2019 Jan 16. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30651334 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Effects of Quercetin on M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization and Oxidative/Antioxidative Balance.Nutrients. 2021 Dec 24;14(1):67. doi: 10.3390/nu14010067. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 35010945 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral CCL2-CCR2 signalling contributes to chronic headache-related sensitization.Brain. 2023 Oct 3;146(10):4274-4291. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad191. Brain. 2023. PMID: 37284790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rittner HL, Mousa SA, Labuz D, Beschmann K, Schäfer M, et al. (2006) Selective local PMN recruitment by CXCL1 or CXCL2/3 injection does not cause inflammatory pain. J Leukoc Biol 79: 1022–1032. - PubMed
-
- Rittner HL, Brack A, Machelska H, Mousa SA, Bauer M, et al. (2001) Opioid peptide expressing leukocytes – Identification, recruitment and simultaneously increasing inhibiton of inflammatory pain. Anesthesiology 95: 500–508. - PubMed
-
- Rollins BJ, Walz A, Baggiolini M (1991) Recombinant human MCP-1/JE induces chemotaxis, calcium flux, and the respiratory burst in human monocytes. Blood 78: 1112–1116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

