Three-dimensional hierarchical plasmonic nano-architecture enhanced surface-enhanced Raman scattering immunosensor for cancer biomarker detection in blood plasma
- PMID: 23659430
- PMCID: PMC3732798
- DOI: 10.1021/nn4018284
Three-dimensional hierarchical plasmonic nano-architecture enhanced surface-enhanced Raman scattering immunosensor for cancer biomarker detection in blood plasma
Abstract
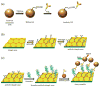
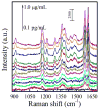
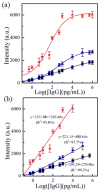
A three-dimensional (3D) hierarchical plasmonic nano-architecture has been designed for a sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) immunosensor for protein biomarker detection. The capture antibody molecules are immobilized on a plasmonic gold triangle nanoarray pattern. On the other hand, the detection antibody molecules are linked to the gold nanostar@Raman reporter@silica sandwich nanoparticles. When protein biomarkers are present, the sandwich nanoparticles are captured over the gold triangle nanoarray, forming a confined 3D plasmonic field, leading to the enhanced electromagnetic field in intensity and in 3D space. As a result, the Raman reporter molecules are exposed to a high density of "hot spots", which amplifies the Raman signal remarkably, improving the sensitivity of the SERS immunosensor. This SERS immunosensor exhibits a wide linear range (0.1 pg/mL to 10 ng/mL) and a low limit of detection (7 fg/mL) toward human immunoglobulin G protein in the buffer solution. This biosensor has been successfully used for detection of the vascular endothelial growth factor in the human blood plasma from clinical breast cancer patient samples.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
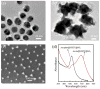
 ) the Au spheres coupled on the Au triangle nano-array, and (
) the Au spheres coupled on the Au triangle nano-array, and (
 ) the Au stars coupled on the Au triangle nano-array.
) the Au stars coupled on the Au triangle nano-array.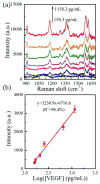
References
-
- Arya SK, Bhansali S. Lung Cancer and Its Early Detection Using Biomarker-Based Biosensors. Chem Rev. 2011;111:6783–6809. - PubMed
-
- Ai K, Zhang B, Lu L. Europium-Based Fluorescence Nanoparticle Sensor for Rapid and Ultrasensitive Detection of an Anthrax Biomarker. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2008;47:1– 6. - PubMed
-
- Trantum JR, Wright DW, Haselton FR. Biomarker-Mediated Disruption of Coffee-Ring Formation as a Low Resource Diagnostic Indicator. Langmuir. 2012;28:2187–2193. - PubMed
-
- Kim DM, Noh HB, Park DS, Ryu SH, Koo JS, Shim YB. Immunosensors for Detection of Annexin II and MUC5AC for Early Diagnosis of Lung Cancer. Biosens Bioelectron. 2009;25:456–462. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosi A, Airò F, Merkoçi A. Enhanced Gold Nanoparticle Based ELISA for a Breast Cancer Biomarker. Anal Chem. 2010;82:1151–1156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

