Differences in imaging characteristics of HPV-positive and HPV-Negative oropharyngeal cancers: a blinded matched-pair analysis
- PMID: 23660291
- PMCID: PMC3951375
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A3524
Differences in imaging characteristics of HPV-positive and HPV-Negative oropharyngeal cancers: a blinded matched-pair analysis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal cancers typically have younger age of onset, limited tobacco exposure, and more favorable prognosis than HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancers. We assessed whether HPV-positive and HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancers have consistent differences in pretreatment imaging characteristics.
Materials and methods: A retrospective review of 136 pretreatment CT examinations of paired HPV-positive and HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancers matched for T stage, tumor subsite, and smoking status was performed with the reviewing radiologist blinded to HPV status and clinical stage. Demographic/clinical characteristics and imaging characteristics of primary lesions and metastatic nodal disease were compared by use of Fisher exact testing. The McNemar χ(2) test was used for the matched-pair analysis.
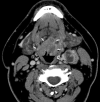
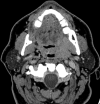
Results: By imaging, HPV-negative tumors were more likely to demonstrate invasion of adjacent muscle (26% versus 6%, P = .013). HPV-positive primary tumors were more likely to be enhancing and exophytic with well-defined borders, whereas HPV-negative primary tumors were more likely to be isoattenuated and demonstrate ill-defined borders, though these results were not statistically significant. HPV-positive tumors were more likely to demonstrate cystic nodal metastases than HPV-negative tumors (36% versus 9%, P = .002).
Conclusions: In this matched and blinded analysis of the imaging differences between HPV-positive and HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancers, HPV-positive carcinomas often had primary lesions with well-defined borders and cystic nodal metastases, whereas HPV-negative primaries more often had poorly defined borders and invasion of adjacent muscle.
Figures


References
-
- Chaturvedi AK, Engels EA, Anderson WF, et al. Incidence trends for human papillomavirus-related and -unrelated oral squamous cell carcinomas in the United States. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:612–19 - PubMed
-
- Carvalho AL, Nishimoto IN, Califano JA, et al. Trends in incidence and prognosis for head and neck cancer in the United States: a site-specific analysis of the SEER database. Int J Cancer 2005;114:806–16 - PubMed
-
- Shiboski CH, Schmidt BL, Jordan RC. Tongue and tonsil carcinoma: increasing trends in the US population ages 20–44 years. Cancer 2005;103:1843–49 - PubMed
-
- Sturgis EM, Ang KK. The epidemic of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer is here: is it time to change our treatment paradigms? J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2011;9:665–73 - PubMed
-
- Sturgis EM, Cinciripini PM. Trends in head and neck cancer incidence in relation to smoking prevalence: an emerging epidemic of human papillomavirus-associated cancers? Cancer 2007;110:1429–35 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
