Tissue distribution, ontogeny, and chemical induction of aldo-keto reductases in mice
- PMID: 23660342
- PMCID: PMC3716307
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.113.051904
Tissue distribution, ontogeny, and chemical induction of aldo-keto reductases in mice
Abstract
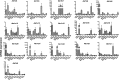
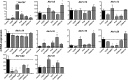
Aldo-keto reductases (Akrs) are a conserved group of NADPH-dependent oxido-reductase enzymes. This study provides a comprehensive examination of the tissue distribution of the 16 substrate-metabolizing Akrs in mice, their expression during development, and whether they are altered by chemicals that activate distinct transcriptional factor pathways. Akr1c6, 1c14, 1c20, and 1c22 are primarily present in liver; Akr1a4, 1c18, 1c21, and 7a5 in kidney; Akr1d1 in liver and kidney; Akr1b7 in small intestine; Akr1b3 and Akr1e1 in brain; Akr1b8 in testes; Akr1c14 in ovaries; and Akrs1c12, 1c13, and 1c19 are expressed in numerous tissues. Liver expression of Akr1d1 and Akr1c is lowest during prenatal and postnatal development. However, by 20 days of age, liver Akr1d1 increases 120-fold, and Akr1c mRNAs increase as much as 5-fold (Akr1c19) to 1000-fold (Akr1c6). Treatment of mice with chemical activators of transcription factors constitutive androgen receptor (CAR), pregnane X receptor (PXR), and the nuclear factor-erythroid-2 (Nrf2) transcription factor alters liver mRNAs of Akrs. Specifically, CAR activation by 1,4-bis[2-(3,5-dichloropyridyloxy)]benzene (TCPOBOP) increases mRNAs of Akr1b7, Akr1c6, Akr1c19, and Akr1d1, whereas PXR activation by 5-pregnenolone-16α-carbonitrile (PCN) increases the mRNA of Akr1b7 and suppresses mRNAs of Akr1c13 and Akr1c20. The Nrf2 activator 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9-dien-28-imidazolide (CDDO-Im) induces mRNAs of Akr1c6 and Akr1c19. Moreover, Nrf2-null and Nrf2 overexpressing mice demonstrate that this induction is Nrf2-dependent.
Figures



References
-
- Cheng X, Maher J, Dieter MZ, Klaassen CD. (2005) Regulation of mouse organic anion-transporting polypeptides (Oatps) in liver by prototypical microsomal enzyme inducers that activate distinct transcription factor pathways. Drug Metab Dispos 33:1276–1282 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

