Perforin deficiency impairs a critical immunoregulatory loop involving murine CD8(+) T cells and dendritic cells
- PMID: 23660960
- PMCID: PMC3695362
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-04-495309
Perforin deficiency impairs a critical immunoregulatory loop involving murine CD8(+) T cells and dendritic cells
Abstract
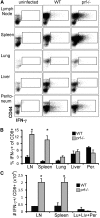
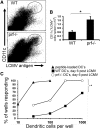
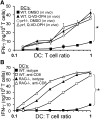
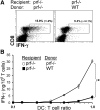
Humans and mice with impaired perforin-dependent cytotoxic function may develop excessive T-cell activation and the fatal disorder hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) after infection. Though cytotoxic lymphocytes can kill antigen-presenting cells, the physiological mechanism of perforin-mediated immune regulation has never been demonstrated in a disease-relevant context. We used a murine model of HLH to examine how perforin controls immune activation, and we have defined a feedback loop that is critical for immune homeostasis. This endogenous feedback loop involves perforin-dependent elimination of rare, antigen-presenting dendritic cells (DCs) by CD8(+) T cells and has a dominant influence on the magnitude of T-cell activation after viral infection. Antigen presentation by a minor fraction of DCs persisted in T-cell- or perforin-deficient animals and continued to drive T-cell activation well beyond initial priming in the latter animals. Depletion of DCs or transfer of perforin-sufficient T cells dampened endogenous DC antigen presentation and T-cell activation, demonstrating a reciprocal relationship between perforin in CD8(+) T cells and DC function. Thus, selective cytotoxic "pruning" of DC populations by CD8(+) T cells limits T-cell activation and protects against the development of HLH and potentially other immunopathological conditions.
Figures


References
-
- Jordan MB, Hildeman D, Kappler J, Marrack P. An animal model of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH): CD8+ T cells and interferon gamma are essential for the disorder. Blood. 2004;104(3):735–743. - PubMed
-
- Pachlopnik Schmid J, Ho CH, Diana J, et al. A Griscelli syndrome type 2 murine model of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). Eur J Immunol. 2008;38(11):3219–3225. - PubMed
-
- Jessen B, Maul-Pavicic A, Ufheil H, et al. Subtle differences in CTL cytotoxicity determine susceptibility to hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in mice and humans with Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Blood. 2011;118(17):4620–4629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

