Bacterial complications of respiratory tract viral illness: a comprehensive evaluation
- PMID: 23661797
- PMCID: PMC3699009
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jit190
Bacterial complications of respiratory tract viral illness: a comprehensive evaluation
Abstract
Background: Respiratory tract infection is one of the most common reasons for hospitalization among adults, and recent evidence suggests that many of these illnesses are associated with viruses. Although bacterial infection is known to complicate viral infections, the frequency and impact of mixed viral-bacterial infections has not been well studied.
Methods: Adults hospitalized with respiratory illness during 3 winters underwent comprehensive viral and bacterial testing. This assessment was augmented by measuring the serum level of procalcitonin (PCT) as a marker of bacterial infection. Mixed viral-bacterial infection was defined as a positive viral test result plus a positive bacterial assay result or a serum PCT level of ≥ 0.25 ng/mL on admission or day 2 of hospitalization.
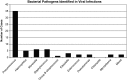
Results: Of 842 hospitalizations (771 patients) evaluated, 348 (41%) had evidence of viral infection. A total of 212 hospitalizations (61%) involved patients with viral infection alone. Of the remaining 136 hospitalizations (39%) involving viral infection, results of bacterial tests were positive in 64 (18%), and PCT analysis identified bacterial infection in an additional 72 (21%). Subjects hospitalized with mixed viral-bacterial infections were older and more commonly received a diagnosis of pneumonia. Over 90% of hospitalizations in both groups involved subjects who received antibiotics. Notably, 4 of 10 deaths among subjects hospitalized with viral infection alone were secondary to complications of Clostridium difficile colitis.
Conclusions: Bacterial coinfection is associated with approximately 40% of viral respiratory tract infections requiring hospitalization. Patients with positive results of viral tests should be carefully evaluated for concomitant bacterial infection. Early empirical antibiotic therapy for patients with an unstable condition is appropriate but is not without risk.
Keywords: bacterial infection; pneumonia; procalcitonin; virus.
Figures
Comment in
-
Serum procalcitonin level, viral polymerase chain reaction analysis, and lower respiratory tract infection.J Infect Dis. 2014 Feb 15;209(4):631-3. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit579. Epub 2013 Nov 11. J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24218499 No abstract available.
-
Reply to Musher et al.J Infect Dis. 2014 Feb 15;209(4):633-5. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit580. Epub 2013 Nov 11. J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24218503 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Falsey AR, Hennessey PA, Formica MA, Cox C, Walsh EE. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in elderly and high-risk adults. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1749–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical