Accessibility and use of essential medicines in health care: Current progress and challenges in India
- PMID: 23662019
- PMCID: PMC3643337
- DOI: 10.4103/0976-500X.107642
Accessibility and use of essential medicines in health care: Current progress and challenges in India
Abstract
Essential Medicine Concept, a major breakthrough in health care, started in 1977 when World Health Organization (WHO) published its first list. Appropriate use of essential medicines is one of the most cost-effective components of modern health care. The selection process has evolved from expert evaluation to evidence-based selection. The first Indian list was published in 1996 and the recent revision with 348 medicines was published in 2011 after 8 years. Health expenditure is less in India as compared to developed countries. India faces a major challenge in providing access to medicines for its 1.2 billion people by focusing on providing essential medicines. In the future, countries will face challenges in selecting high-cost medicines for oncology, orphan diseases and other conditions. There is a need to develop strategies to improve affordable access to essential medicines under the current health care reform.
Keywords: Accessibility; India; essential medicines; health expenditures.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


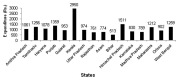
References
-
- Essential Medicines and Pharmaceutical Policies. World Health Organization: Regional office for eastern Mediterranean. [Last cited on 2010 Oct 21]. Available from: http://www.emro.who.int/emp/medicines.htm .
-
- Wertheimer AI, Santella TM. Innovation and the WHO's essential medicines list: Giving credit where credit is due. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2007;3:137–44. - PubMed
-
- WHO Technical Report Series 914. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2003. The selection and use of essential medicines. Report of WHO expert committee, 2002 (including the 12th Model List of Essential Medicines) - PubMed
-
- Regional workshop on recent developments in essential medicines. World Health Organization Colombo, Sri Lanka. 2007. [Last cited on 2011 Nov o2]. Available from: http://www.searo.who.int/LinkFiles/Meetings_EDM_RegionalWorkshop_SRL2Nov... .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
