Comparison of the efficacy and tolerability of ivabradine and ranolazine in patients of chronic stable angina pectoris
- PMID: 23662022
- PMCID: PMC3643340
- DOI: 10.4103/0976-500X.107663
Comparison of the efficacy and tolerability of ivabradine and ranolazine in patients of chronic stable angina pectoris
Abstract
Introduction: To compare the efficacy and tolerability of Ivabradine (IVA) and Ranolazine (RAN) in chronic angina patients.
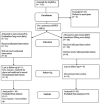
Materials and methods: This was a follow-on, open-label trial conducted in a tertiary care hospital of Uttarakhand. Thirty patients each taking IVA 5 mg twice daily or RAN 500 mg twice daily were distributed to the respective groups. Patients were asked to fill a pretested questionnaire on frequency of anginal attacks and adverse reactions before and 2, 4 and 8 weeks after taking the respective medicines. Their blood pressure, heart rate and routine hematological and biochemical estimations were performed at baseline and after intervention. Results were statistically analyzed using different statistical tests, with P < 0.05 considered as significant.
Results: There was no significant difference in the frequency of anginal attacks per week between the groups. The adverse drug reactions (ADRs) reported in the IVA group were dizziness (30%), headache (16.6%), backache (16.6%), vertigo (13.3%), blurred vision (13.3%), muscle cramps (10%), arthralgia (10%), cough and dyspnea (6.6%), hypersensitivity rash (6.6%), fever (3.3%) and nausea (3.3%). The ADRs in the RAN group were nausea (26.6%), dizziness (23.3%), vomiting (3.3%), constipation (3.3%) and vertigo (3.3%). The blood pressure, heart rate and routine hematological and biochemical evaluations did not show any significant difference in the pre-post values. IVA significantly decreased the resting heart rate after eight weeks of intervention.
Conclusions: Both antianginal agents appeared equiactive. However, RAN had a better safety and tolerability profile than IVA. Serum sickness-like reaction was an adverse event noticed with IVA, which needs causality establishment.
Keywords: Antianginals; dizziness; equiefficacious; nausea; serum sickness-like reaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of ranolazine with atenolol, amlodipine, or diltiazem on exercise tolerance and angina frequency in patients with severe chronic angina: a randomized controlled trial.JAMA. 2004 Jan 21;291(3):309-16. doi: 10.1001/jama.291.3.309. JAMA. 2004. PMID: 14734593 Clinical Trial.
-
Antianginal efficacy of ranolazine when added to treatment with amlodipine: the ERICA (Efficacy of Ranolazine in Chronic Angina) trial.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006 Aug 1;48(3):566-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.05.044. Epub 2006 Jun 15. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 16875985 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of a metabolic modulator drug in chronic stable angina: review of evidence from clinical trials.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Sep;9 Suppl 1:S47-64. doi: 10.1177/107424840400900105. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15378131
-
Ranolazine: a review of its use as add-on therapy in patients with chronic stable angina pectoris.Drugs. 2013 Jan;73(1):55-73. doi: 10.1007/s40265-012-0005-z. Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23329466 Review.
-
Ranolazine: a review of its use in chronic stable angina pectoris.Drugs. 2006;66(5):693-710. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200666050-00010. Drugs. 2006. PMID: 16620147 Review.
Cited by
-
The HCN Channel Blocker ZD7288 Induces Emesis in the Least Shrew (Cryptotis parva).Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 29;12:647021. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.647021. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33995059 Free PMC article.
-
Ranolazine Versus Allopurinol for Eligible Symptomatic Patients With a History of Angioplasty: Comparative Efficacy Study.Interact J Med Res. 2022 Aug 17;11(2):e39778. doi: 10.2196/39778. Interact J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35976197 Free PMC article.
-
Good! Is it the best???J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2013 Jul;4(3):220-1. doi: 10.4103/0976-500X.114611. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 23960432 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Ranolazine and Ivabradine: two different modalities to act against ischemic heart disease.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2016 Apr;10(2):98-102. doi: 10.1177/1753944716636042. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2016. PMID: 26944071 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Murray CJL, Lopez AD. The global burden of disease: A comprehensive assessment of mortality and disability from diseases, injuries, and risk factors in 1990 and projected to 2020.Cambridge, Harvard School of Public Health on behalf of the World Health Organization and The World Bank, 1996 (Global Burden of Disease and Injury Series, Vol. I)
-
- McBride BF, White CM. Ranolazine: A novel metabolic modulator for the treatment of chronic stable angina. Formulary. 2003;38:461–4.
-
- Riccioni G. Ivabradine: From molecular basis to clinical effectiveness. Adv Ther. 2010;27:160–7. - PubMed
-
- Simon L, Ghaleh B, Puybasset L, Guidicelli JF, Berdeaux A. Coronary and haemodynamic effects of S16257, a new bradycardic agent, in resting and exercising conscious dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995;275:659–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous