Efficacy and Tolerability of Peginterferon α -2a and Peginterferon α -2b, Both plus Ribavirin, for Chronic Hepatitis C: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 23662098
- PMCID: PMC3639641
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/739029
Efficacy and Tolerability of Peginterferon α -2a and Peginterferon α -2b, Both plus Ribavirin, for Chronic Hepatitis C: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
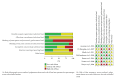
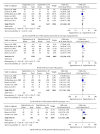
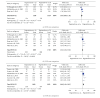
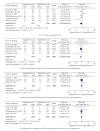
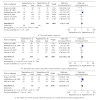
Background. The efficacy and tolerability of peginterferon α -2a and peginterferon α -2b in chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients remain controversial. Methods. PubMed, Ovid, and Cochrane libraries were electronically searched until August 30, 2012. Studies that met the inclusion criteria were systematically evaluated by two reviewers independently. Results. The overall sustained virologic response (SVR) rate of the peginterferon α -2a group was significantly higher than that of the peginterferon α -2b group (46.7% versus 42.4%, P value = 0.01). The same tendency was observed for naïve, genotype 1/4, and genotype 2/3 patients. The early virologic response (EVR) and end-of-treatment response (ETR) rates were significantly higher in the peginterferon α -2a group than in the peginterferon α -2b group (56.1% versus 49.8%, P < 0.0001; 67.9% versus 56.6%, P < 0.00001, resp.). Peginterferon α -2a had a significantly lower discontinuation rate than peginterferon α -2b (27.9% versus 33.9%, P < 0.0001) in naïve patients. In both naïve CHC and hepatitis C virus genotype 1 patients, peginterferon α -2a had a higher relapse rate than peginterferon α -2b. Conclusions. Peginterferon α -2a has superior efficacy with higher EVR, ETR, and SVR than peginterferon α -2b for CHC patients, both plus ribavirin. Peginterferon α -2a might obtain a similar or even lower discontinuation rate than peginterferon α -2b. However, peginterferon α -2a had a higher relapse rate than peginterferon α -2b.
Figures
References
-
- Omata M, Kanda T, Yu ML, et al. APASL consensus statements and management algorithms for hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology International. 2012;6:409–435. - PubMed
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines:management of hepatitis C virus infection. Journal of Hepatology. 2011;55(2):245–264. - PubMed
-
- Schaefer EAK, Chung RT. Anti-hepatitis C virus drugs in development. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:1340–1350. - PubMed
-
- Yenice N, Mehtap O, Gümrah M, Arican N. The efficacy of pegylated interferon alpha 2a or 2b plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients. Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology. 2006;17(2):94–98. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

