The neurobiological correlates of childhood adversity and implications for treatment
- PMID: 23662634
- PMCID: PMC4467688
- DOI: 10.1111/acps.12143
The neurobiological correlates of childhood adversity and implications for treatment
Abstract
Objective: This article provides an overview of research on the neurobiological correlates of childhood adversity and a selective review of treatment implications.
Method: Findings from a broad array of human and animal studies of early adversity were reviewed.
Results: Topics reviewed include neuroendocrine, neurotrophic, neuroimaging, and cognitive effects of adversity, as well as genetic and epigenetic influences. Effects of early-life stress on treatment outcome are considered, and development of treatments designed to address the neurobiological abnormalities is discussed.
Conclusion: Early adversity is associated with abnormalities of several neurobiological systems that are implicated in the development of psychopathology and other medical conditions. Early-life stress negatively impacts treatment outcome, and individuals may require treatments that are specific to this condition.
Keywords: childhood abuse; early-life stress; neurobiology; treatment.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
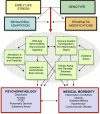
Figures
References
-
- DOZIER M, ALBUS K, FISHER PA, SEPULVEDA S. Interventions for foster parents: implications for developmental theory. Dev Psychopathol. 2002;14:843–860. - PubMed
-
- LUPIEN SJ, MCEWEN BS, GUNNAR MR, HEIM C. Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:434–445. - PubMed
-
- MCCRORY E, DE BRITO SA, VIDING E. Research review: the neurobiology and genetics of maltreatment and adversity. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2010;51:1079–1095. - PubMed
-
- KAFFMAN A, MEANEY MJ. Neurodevelopmental sequelae of postnatal maternal care in rodents: clinical and research implications of molecular insights. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2007;48:224–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

