Streptococcal-vimentin cross-reactive antibodies induce microvascular cardiac endothelial proinflammatory phenotype in rheumatic heart disease
- PMID: 23663103
- PMCID: PMC3949629
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12135
Streptococcal-vimentin cross-reactive antibodies induce microvascular cardiac endothelial proinflammatory phenotype in rheumatic heart disease
Abstract
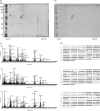
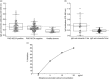
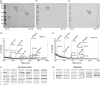
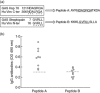
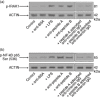
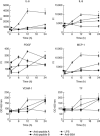
Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) is characterized by the presence of anti-streptococcal group A antibodies and anti-endothelial cell antibodies (AECA). Molecular mimicry between streptococcal antigens and self proteins is a hallmark of the pathogenesis of rheumatic fever. We aimed to identify, in RHD patients, autoantibodies specific to endothelial autoantigens cross-reactive with streptococcal proteins and to evaluate their role in inducing endothelial damage. We used an immunoproteomic approach with endothelial cell-surface membrane proteins in order to identify autoantigens recognized by AECA of 140 RHD patients. Cross-reactivity of purified antibodies with streptococcal proteins was analysed. Homologous peptides recognized by serum cross-reactive antibodies were found through comparing the amino acid sequence of streptococcal antigens with human antigens. To investigate interleukin (IL)-1R-associated kinase (IRAK1) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation, we performed a Western blot analysis of whole extracts proteins from unstimulated or stimulated human microvascular cardiac endothelial cells (HMVEC-C). Adhesion molecule expression and release of proinflammatory cytokines and growth factors were studied by multiplex bead based immunoassay kits. We observed anti-vimentin antibodies in sera from 49% RHD AECA-positive patients. Cross-reactivity of purified anti-vimentin antibodies with heat shock protein (HSP)70 and streptopain streptococcal proteins was shown. Comparing the amino acid sequence of streptococcal HSP70 and streptopain with human vimentin, we found two homologous peptides recognized by serum cross-reactive antibodies. These antibodies were able to stimulate HMVEC-C inducing IRAK and NF-κB activation, adhesion molecule expression and release of proinflammatory cytokines and growth factors. In conclusion, streptococcal-vimentin cross-reactive antibodies were able to activate microvascular cardiac endothelium by amplifying the inflammatory response in RHD.
Keywords: anti-endothelial cell autoantibodies; rheumatic heart disease; vimentin.
© 2013 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of cardiac autoantigens in human heart cDNA libraries using acute rheumatic fever sera.J Autoimmun. 1994 Apr;7(2):243-61. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1994.1019. J Autoimmun. 1994. PMID: 8037842
-
Mimicry in recognition of cardiac myosin peptides by heart-intralesional T cell clones from rheumatic heart disease.J Immunol. 2006 May 1;176(9):5662-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.9.5662. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16622036
-
Molecular mimicry between streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin B and endothelial cells.Lab Invest. 2010 Oct;90(10):1492-506. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.93. Epub 2010 May 10. Lab Invest. 2010. PMID: 20458278
-
Streptococcus and rheumatic fever.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012 Jul;24(4):408-16. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32835461d3. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22617826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T cell subsets: an integral component in pathogenesis of rheumatic heart disease.Immunol Res. 2018 Feb;66(1):18-30. doi: 10.1007/s12026-017-8978-z. Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29170852 Review.
Cited by
-
Alpha-1-antitrypsin in serum exosomes and pericardial fluid exosomes is associated with severity of rheumatic heart disease.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Jun;478(6):1383-1396. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04595-x. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36318408
-
Update on Post-Streptococcal Reactive Arthritis: Narrative Review of a Forgotten Disease.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021 Feb 10;23(3):19. doi: 10.1007/s11926-021-00982-3. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33569668 Review.
-
Cell surface detection of vimentin, ACE2 and SARS-CoV-2 Spike proteins reveals selective colocalization at primary cilia.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 29;12(1):7063. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11248-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35487944 Free PMC article.
-
Is COVID-19 a proteiform disease inducing also molecular mimicry phenomena?Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020 May;25(3):381-382. doi: 10.1007/s12192-020-01112-1. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020. PMID: 32314313 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Anti-endothelial cell antibodies in pathogenesis of vasculitis.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 30;16:1567293. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1567293. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40370444 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Special Writing Group of the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease of the Council on cardiovascular Disease in the Young of the American Heart Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis of rheumatic fever. Jones criteria, 1992 update. JAMA. 1992;268:2069–2073. - PubMed
-
- Smith MT, Zurynski Y, Lester-Smith D, Elliott E, Carapetis J. Rheumatic fever – identification, management and secondary prevention. Aust Fam Physician. 2012;41:31–35. - PubMed
-
- Carapetis JR, Steer AC, Mulholland EK, Weber M. The global burden of group A streptococcal diseases. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:685–694. - PubMed
-
- Marijon E, Ou P, Celermajer DS, et al. Prevalence of rheumatic heart disease detected by echocardiographicic screening. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:470–476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

