Exploring the larval transcriptome of the common sole (Solea solea L.)
- PMID: 23663263
- PMCID: PMC3659078
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-315
Exploring the larval transcriptome of the common sole (Solea solea L.)
Abstract
Background: The common sole (Solea solea) is a promising candidate for European aquaculture; however, the limited knowledge of the physiological mechanisms underlying larval development in this species has hampered the establishment of successful flatfish aquaculture. Although the fact that genomic tools and resources are available for some flatfish species, common sole genomics remains a mostly unexplored field. Here, we report, for the first time, the sequencing and characterisation of the transcriptome of S. solea and its application for the study of molecular mechanisms underlying physiological and morphological changes during larval-to-juvenile transition.
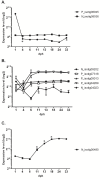
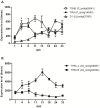
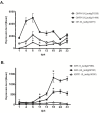
Results: The S. solea transcriptome was generated from whole larvae and adult tissues using the Roche 454 platform. The assembly process produced a set of 22,223 Isotigs with an average size of 726 nt, 29 contigs and a total of 203,692 singletons. Of the assembled sequences, 75.2% were annotated with at least one known transcript/protein; these transcripts were then used to develop a custom oligo-DNA microarray. A total of 14,674 oligonucleotide probes (60 nt), representing 12,836 transcripts, were in situ synthesised onto the array using Agilent non-contact ink-jet technology. The microarray platform was used to investigate the gene expression profiles of sole larvae from hatching to the juvenile form. Genes involved in the ontogenesis of the visual system are up-regulated during the early stages of larval development, while muscle development and anaerobic energy pathways increase in expression over time. The gene expression profiles of key transcripts of the thyroid hormones (TH) cascade and the temporal regulation of the GH/IGF1 (growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor I) system suggest a pivotal role of these pathways in fish growth and initiation of metamorphosis. Pre-metamorphic larvae display a distinctive transcriptomic landscape compared to previous and later stages. Our findings highlighted the up-regulation of gene pathways involved in the development of the gastrointestinal system as well as biological processes related to folic acid and retinol metabolism. Additional evidence led to the formation of the hypothesis that molecular mechanisms of cell motility and ECM adhesion may play a role in tissue rearrangement during common sole metamorphosis.
Conclusions: Next-generation sequencing provided a good representation of the sole transcriptome, and the combination of different approaches led to the annotation of a high number of transcripts. The construction of a microarray platform for the characterisation of the larval sole transcriptome permitted the definition of the main processes involved in organogenesis and larval growth.
Figures


Similar articles
-
De novo assembly, characterization and functional annotation of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) and common sole (Solea solea) transcriptomes: integration in a database and design of a microarray.BMC Genomics. 2014 Nov 3;15(1):952. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-952. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25366320 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic resources for a commercial flatfish, the Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis): EST sequencing, oligo microarray design, and development of the Soleamold bioinformatic platform.BMC Genomics. 2008 Oct 30;9:508. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-508. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18973667 Free PMC article.
-
Ontogenetic onset of immune-relevant genes in the common sole (Solea solea).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016 Oct;57:278-292. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.08.044. Epub 2016 Aug 21. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27554393
-
Metamorphosis-associated immune system maturation in Senegalese sole.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2025 Jun;369:114755. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2025.114755. Epub 2025 May 31. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40456456 Review.
-
Orchestrating change: The thyroid hormones and GI-tract development in flatfish metamorphosis.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2015 Sep 1;220:2-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2014.06.012. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 24975541 Review.
Cited by
-
Ontogeny of Expression and Activity of Digestive Enzymes and Establishment of gh/igf1 Axis in the Omnivorous Fish Chelon labrosus.Animals (Basel). 2020 May 18;10(5):874. doi: 10.3390/ani10050874. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32443440 Free PMC article.
-
De novo assembly, characterization and functional annotation of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) and common sole (Solea solea) transcriptomes: integration in a database and design of a microarray.BMC Genomics. 2014 Nov 3;15(1):952. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-952. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25366320 Free PMC article.
-
An improved de novo assembling and polishing of Solea senegalensis transcriptome shed light on retinoic acid signalling in larvae.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 26;10(1):20654. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77201-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33244091 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic transcriptome sequencing and analysis during early development in the bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis).BMC Genomics. 2019 Oct 28;20(1):781. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6181-4. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31660854 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray: a global analysis of biomineralization-related gene expression profiles during larval development in the pearl oyster, Pinctada fucata.BMC Genomics. 2015 Apr 19;16(1):325. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1524-2. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25927556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mazurais D, Darias M, Zambonino-Infante JL, Cahu CL. Transcriptomics for understanding marine fish larval development. Can J Zool. 2011;89:599–611. doi: 10.1139/z11-036. - DOI
-
- Bonaldo A, Parma L, Badiani A, Serratore P, Gatta PP. Very early weaning of common sole (Solea solea L.) larvae by means of different feeding regimes and three commercial microdiets: influence on performances, metamorphosis development and tank hygiene. Acquaculture. 2011;321:237–244. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.09.007. - DOI
-
- Agulleiro MJ, Nguis V, Cañavate JP, Martínez-Rodríguez G, Mylonas CC, Cerdà J. Induction of spawning of captive-reared Senegal sole (Solea senegalensis) using different delivery systems for gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist. Aquaculture. 2006;257(1–4):511–524.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

