Economic evaluation of agomelatine relative to other antidepressants for treatment of major depressive disorders in Greece
- PMID: 23663281
- PMCID: PMC3654993
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6963-13-173
Economic evaluation of agomelatine relative to other antidepressants for treatment of major depressive disorders in Greece
Abstract
Background: Major depressive disorder (MDD) constitutes an important public health problem, as it is highly prevalent in the industrialized world and it is associated with substantial economic consequences for patients, health care providers, insurance and social security organizations and employers. To conduct an economic evaluation comparing agomelatine with other commonly used alternatives for treating patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) in Greece.
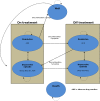
Methods: An existing international Markov model designed to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of agomelatine was adapted to the Greek setting. It reflects six different health states, in which patients may move on a monthly basis. The analysis was undertaken from a societal perspective. Transition probabilities, utilities and costs assigned to each health state were extracted from the published literature, government sources and expert opinion. Data reflects the year 2012 and was discounted using a rate of 3.5%. Probabilistic analysis was undertaken to deal with uncertainty.
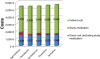
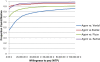
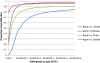
Results: Base case analyses revealed that agomelatine is a dominant therapy for MDD relative to escitalopram, fluoxetine and sertraline, and it appeared to be cost-effective compared to venlafaxine (ICER: €547/QALY). Agomelatine remained a dominant treatment against generic sertraline and fluoxetine, and it appeared to be a cost-effective alternative compared to generic venlafaxine and escitalopram (ICER: €1,446/QALY and €3,303/QALY, respectively). Excluding the indirect cost from the analysis, agomelatine remained a cost-effective alternative over all comparators. In the probabilistic sensitivity analysis agomelatine was dominant in 44.5%, 89.6%, 70.6% and 84.6% of simulated samples against branded venlafaxine, escitalopram, fluoxetine and sertraline, respectively.
Conclusion: The present evaluation indicates that agomelatine is either a dominant or a cost-effective alternative relative to branded or generic alternatives, in Greece.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of pharmaceutical treatment options in the first-line management of major depressive disorder in Belgium.Pharmacoeconomics. 2014 May;32(5):479-93. doi: 10.1007/s40273-014-0138-x. Pharmacoeconomics. 2014. PMID: 24554474 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-utility analysis of vortioxetine versus agomelatine, bupropion SR, sertraline and venlafaxine XR after treatment switch in major depressive disorder in Finland.Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2017 Jun;17(3):293-302. doi: 10.1080/14737167.2017.1240617. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2017. PMID: 27680105
-
Switching to sertraline or venlafaxine after failure of SSRIs treatment in major depressive disorder: an economic evaluation of the STAR*D trial.J Med Assoc Thai. 2012 May;95 Suppl 5:S29-37. J Med Assoc Thai. 2012. PMID: 22934442
-
Escitalopram: a pharmacoeconomic review of its use in depression.Pharmacoeconomics. 2003;21(16):1185-209. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200321160-00004. Pharmacoeconomics. 2003. PMID: 14594439 Review.
-
Efficacy of agomelatine in major depressive disorder: meta-analysis and appraisal.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012 Apr;15(3):417-28. doi: 10.1017/S1461145711001301. Epub 2011 Aug 23. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21859514 Review.
Cited by
-
The Incidence and Costs of Adverse Events Associated with Antidepressants: Results from a Systematic Review, Network Meta-Analysis and Multi-Country Economic Model.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022 Jun 7;18:1133-1143. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S356414. eCollection 2022. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022. PMID: 35698594 Free PMC article.
-
A Promising Approach to Optimizing Sequential Treatment Decisions for Depression: Markov Decision Process.Pharmacoeconomics. 2022 Nov;40(11):1015-1032. doi: 10.1007/s40273-022-01185-z. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Pharmacoeconomics. 2022. PMID: 36100825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Model-Based Economic Evaluation of Treatments for Depression: A Systematic Literature Review.Pharmacoecon Open. 2017 Sep;1(3):149-165. doi: 10.1007/s41669-017-0014-7. Pharmacoecon Open. 2017. PMID: 29441493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cost-utility analysis of esketamine and electroconvulsive therapy in adults with treatment-resistant depression.BMC Psychiatry. 2021 Dec 7;21(1):610. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03601-8. BMC Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34876085 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Time-Course, Dose-Effect, and Influencing Factors of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Acute Adult Patients With Major Depression.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020 Feb 1;23(2):76-87. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyz062. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31774497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sobocki P, Jonsson B, Angst J, Rehnberg C. Cost of depression in Europe. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2006;9:87–98. - PubMed
-
- Sobocki P, Ekman M, Agren H, Runeson B, Jonsson B. The mission is remission: health economic consequences of achieving full remission with antidepressant treatment for depression. Int J Clin Pract. 2006;60:791–798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

