ST9 MRSA strains carrying a variant of type IX SCCmec identified in the Thai community
- PMID: 23663295
- PMCID: PMC3658997
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-214
ST9 MRSA strains carrying a variant of type IX SCCmec identified in the Thai community
Abstract
Background: Infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Thailand occur most frequently in healthcare facilities. However, reports of community-associated MRSA are limited.
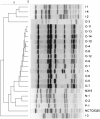
Methods: We characterized 14 MRSA isolates from outpatients (O-1 to O-14) by phenotypic and genotypic methods and compared them with 5 isolates from inpatients (I-1 to I-5). Thai MRSA isolates from a healthcare worker (N-1) and a pig (P-1) were also included as ST9 MRSA strains from other sources.
Results: All MRSA isolates from the outpatients and inpatients were multidrug-resistant (resistant to ≥3 classes of antimicrobials). All of them except strains O-2 and I-3 carried type III SCCmec and belonged to agrI, coagulase IV, spa type t037 or t233, which related to ST239. The strain O-2 (JCSC6690) carried type IX SCCmec and belonged to agrII, coagulaseXIc, spa type t337 and ST9, whereas the strain I-3 carried a type III SCCmec and belonged to ST1429. Nucleotide sequence determination revealed that the type IX SCCmec element in strain O-2 was distinct from that in a Thai ST398 strain (JCSC6943) previously identified in 2011; nucleotide identities of ccrA and ccrB were 93 and 91%, respectively and several open reading frames (ORFs) at the joining regions were different. PCR experiments suggested that strain O-2 and N-1 carried similar SCCmec element, whereas that of strain P-1 was different, suggesting that distinct ST9-MRSA-IX clones might be spreading in this province.
Conclusions: The SCCmecIX-ST9 MRSA clones of distinct SCCmec subtypes might have emerged in the Thai community and might also have disseminated into the hospital.
Figures

References
-
- Katayama Y, Ito T, Hiramatsu K. Genetic organization of the chromosome region surrounding mecA in clinical staphylococcal strains: role of IS431-mediated mecI deletion in expression of resistance in mecA-carrying, low-level methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001;45(7):1955–1963. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.7.1955-1963.2001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Turlej A, Hryniewicz W, Empel J. Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec (SCCmec) classification and typing methods: an overview. Pol J Microbiol. 2011;60(2):95–103. - PubMed
-
- Song JH, Hsueh PR, Chung DR, Ko KS, Kang CI, Peck KR, Yeom JS, Kim SW, Chang HH, Kim YS, Jung SI, Son JS, So TM, Lalitha MK, Yang Y, Huang SG, Wang H, Lu Q, Carlos CC, Pepera JA, Chiu CH, Liu JW, Chongthaleong A, Thamlikikul V, Van PH. Spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus between the community and the hospitals in Asian countries: an ANSORP study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66(5):1061–1069. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr024. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

